Abstract
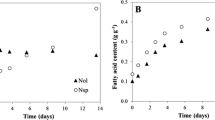
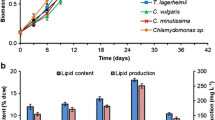
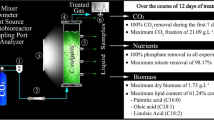
The aim of the study was to identify the optimum cultivation conditions for the microalgal growth and lipid production of the oleaginous microalga Chlorella pyrenoidosa Chick (IPPAS C2). Moreover, an appropriate NO3− concentration in the cultivation medium for maximized lipid accumulation was determined. The experimental design involved a biphasic cultivation strategy with an initial biomass accumulating phase under optimized light (400 μmol/m2 per s), temperature (25 °C), and elevated CO2 concentration in the air mixture (3%), followed by a mid-elevated CO2 concentration (0.5%) for lipid induction. The highest lipid yields of 172.47 ± 18.1 and 179.65 ± 25.4 mg/L per day were detected for NO3− concentrations of 100 and 150 mg/L. The optimization approach presented here led not only to the maximization of lipid yield but also to the development of a biphasic cultivation strategy easily applicable to the cultivation process without the necessity for algal cell harvesting between the first and second cultivation phases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baroni EG, Yap KY, Webley PA, Scales PJ, Martin GJO (2019) The effect of nitrogen depletion on the cell size, shape, density and gravitational settling of Nannochloropsis salina, Chlorella sp. (marine) and Haematococcus pluviatilis. Algal Res 39:1–10
Barsanti L, Gualtieri P (2018) Is exploitation of microalgae economically and energetically sustainable? Algal Res 31:107–115
Berges JA, Charlebois DO, Mauzerall DC, Falkowski PG (1996) Differential effects of nitrogen limitation on photosynthetic efficiency of photosystem I and II in microalgae. Plant Physiol 110:689–696
Breuer G, Lamers PP, Martens DE, Draaisma RB, Wijffels RH (2013) Effect of light intensity, pH, and temperature on triacylglycerol (TAG) accumulation induced by nitrogen starvation in Scenedesmus obliquus. Bioresour Technol 143:1–9
Cho K, Cho DH, Heo J, Kim U, Lee YJ, Choi DY, Kim HS (2019) Nitrogen modulation under chemostat cultivation mode induces biomass and lipid production by Chlorella vulgaris and reduces antenna pigment accumulation. Bioresour Technol 281:118–125
Converti A, Casazza AA, Ortiz EY, Perego P, Del Borghi M (2009) Effect of temperature and nitrogen concentration on the growth and lipid content of Nannochloropsis oculata and Chlorella vulgaris for biodiesel production. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 48(11):46–51
Cui Y, Thomas-Hall SR, Schenk PM (2019) Phaeodactylum tricornutum microalgae as a rich source of omega-3 oil: progress in lipid induction techniques towards industry adoption. Food Chem 297, Epub 2019 Jun 3:124937
Dean AP, Sigee DC, Estrada B, Pittman JK (2010) Using FTIR spectroscopy for rapid determination of lipid accumulation in response to nitrogen limitation in freshwater microalgae. Bioresour Technol 101:4499–4507
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Griffiths MJ, van Hille RP, Harrison STL (2014) The effect of nitrogen limitation on lipid productivity and cell composition in Chlorella vulgaris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol:2345–2356
He Q, Yang H, Wu L, Hu C (2015) Effect of light intensity on physiological changes, carbon allocation and neutral lipid accumulation in oleaginous microalgae. Bioresour Technol 191:219–228
Hu X, Liu B, Deng Y, Bao X, Yang A, Zhou J (2019) A novel two-stage culture strategy used to cultivate Chlorella vulgaris for increasing the lipid productivity. Sep Purif Technol 211:816–822
Kanaga K, Pandey A, Kumar S, Geetanjali (2016) Multi-objective optimization of media nutrients for enhanced production of algae biomass and fatty acid biosynthesis from Chlorella pyrenoidosa NCIM 2738. Bioresour Technol 200:940–950
Kawamura K, Sumii K, Matsumoto M, Nakase D, Kosaki Y (2018) Determining the optimal cultivation strategy for microalgae for biodiesel production using flow cytometric monitoring and mathematical modeling. Biomass Bioenergy 117:24–31
Krzeminska I, Piasecka A, Nosalewicz A, Simionato D, Wawrzykowski J (2015) Alterations of the lipid content and fatty acid profile of Chlorella protothecoides under different light intensities. Bioresour Technol 196:72–77
Lam MK, Lee KT (2014) Cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris in a pilot-scale sequential-baffled column photobioreactor for biomass and biodiesel production. Energy Convers Manag 88:399–410
Li T, Xu J, Gao B, Xiang W, Li A, Zhang C (2016) Morphology, growth, biochemical composition and photosynthetic performance of Chlorella vulgaris (Trebouxiophyceae) under low and high nitrogen supplies. Algal Res 16:481–491
Liu J, Vyverman W (2015) Differences in nutrient uptake capacity of the benthic filamentous algae Cladophora sp., Klebsormidium sp. and Pseudanabaena sp. under varying N/P conditions. Bioresour Technol 179:234–242
Mata TM, Martins AA, Caetano NS (2010) Microalgae for biodiesel production and other aplications: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 14:217–232
Nayak M, Suh WI, Chang YK, Lee B (2019) Exploration of two-stage cultivation strategies using nitrogen starvation to maximize the lipid productivity in Chlorella sp. HS2. Bioresour Technol 276:110–118
Nedbal L, Trtílek M, Červený J, Komárek O, Pakrasi HB (2008) A photobioreactor system for precision cultivation of photoautotrophic microorganisms and for high content analysis of suspension dynamics. Biotechnol Bioeng 100/5:902–910
Ördög V, Stirk WA, Bálint P, Aremu AO, Okem A, Lóvázs C, Molnár Z, van Staden J (2016) Effect of temperature and nitrogen concentration on lipid productivity and fatty acid composition in three Chlorella strains. Algal Res 16:141–149
Qiu R, Gao S, Lopez PA, Ogden KL (2017) Effects of pH on cell growth, lipid production and CO2 addition of microalgae Chlorella sorokiniana. Algal Res 28:192–199
Rai MP, Gautom T, Sharma N (2015) Effect of salinity, pH, light intensity on growth and lipid production of microalgae for bioenergy application. OnLine J Biol Sci 15(4):260–267
Sajjadi B, Chen WY, Raman AAA, Ibrahim S (2018) Microalgae lipid and biomass for biofuel production: a comprehensive review on lipid enhancement strategies and their effects on fatty acid composition. Renew Sust Energ Rev 97:200–232
Sakarika M, Kornaros M (2017a) Effect of pH on growth and lipid accumulation kinetics of the microalga Chlorella vulgaris grown heterotrophically under sulfur limitation. Bioresour Technol 219:694–701
Sakarika M, Kornaros M (2017b) Kinetics of growth and lipids accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris during batch heterotrophic cultivation: effect of different nutrient limitation strategies. Bioresour Technol 243:356–365
Skau LF, Andersen T, Thrane JE, Hessen DO (2017) Growth, stoichiometry and cell size; temperature and nutrient responses in haptophytes. PeerJ 5(e3743):1–18
Spolaore P, Joannis-Cassan C, Duran E, Isambert A (2006) Commercial applications of microalgae. J Biosci Bioeng 101/2:87–96
Stanier RY, Kunisawa R, Mandel M, Cohen-Bazire G (1971) Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (Order Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev 35:171–205
Sukačová K, Búzová D, Trávníček P, Červený J, Vítězová M, Vítěz T (2019) Optimization of microalgal growth and cultivation parameters for increasing bioenergy potential: case study using the oleaginous microalga Chlorella pyrenoidosa Chick (IPPAS C2). Algal Res 40:1–8
Tang H, Chen M, Garcia MED, Abunasser N, Simon Ng KY (2011) Culture of microalgae Chlorella minutissima for biodiesel feedstock production. Biotechnol Bioeng 108(10):2280–2287
Tran NAT, Padula MP, Evenhuis CR, Commault AS (2016) Proteomic and biophysical analyses reveal a metabolic shift in nitrogen deprived Nannochloropsis oculata. Algal Res 19:1–11
Wan X, Chao A, Chen Y, Gao XX, Zhong RT, Liu B, Chen X, Zhao C (2020) Physicochemical characterization of a polysaccharide from green microalga Chlorella pyrenoidosa and its hypolipidemic activity via gut microbiota regulation in rats. J Agric Food Chem 68/ 5:1186–1197
Yap BHJ, Crawford SA, Dagastine RR, Scales PJ, Martin GJO (2016) Nitrogen deprivation of microalgae: effect on cell size, cell wall thickness, cell strength, and resistance to mechanical disruption. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43/12:1671–1680
Zavřel T, Sinetova MA, Búzová D, Literáková P, Červený J (2015) Characterization of a model cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 autotrophic growth in a flat-panel photobioreactor. Eng Life Sci 15:122–132
Zhang O, Wang T, Hong Y (2014) Investigation of initial pH effects on growth of an oleaginous microalgae Chlorella sp HQ for lipid production and nutrient uptake. Water Sci Technol 70:712–719
Funding
This study was funded by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic (OP RDE grant number CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_026/0008413 “Strategic Partnership for Environmental Technologies and Energy Production” and the National Sustainability Program I (NPU I) grant number LO1415).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sukačová, K., Búzová, D. & Červený, J. Biphasic optimization approach for maximization of lipid production by the microalga Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Folia Microbiol 65, 901–908 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-020-00800-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-020-00800-w