Abstract
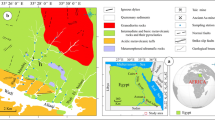
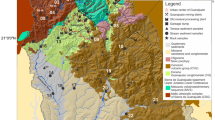
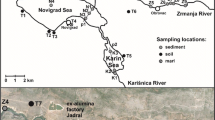
Over the past 100 years, the area along the River Bílina has been influenced by open-cast brown-coal mining, coal processing, petroleum refineries, and chemical plants. As a result, the extensive industrial activity has changed the overall character as well as the morphology of the landscape. A survey was underway to investigate the occurrence and distribution of various elements in the sediments of the River Bílina—a tributary of the River Elbe, a watercourse running through the Czech Republic and Germany—in order to discern the natural background from anthropogenic pollution. The study evaluated the content of selected elements (As, Zn, Pb, Cr, Ni, V, and Cu) in stream sediments of the River Bílina. Samples were taken at 20 sampling sites throughout the 82-km-long watercourse. For all the samples, the content of the elements was determined using ICP-MS after each of the sample was digested using HF and HNO3. The results of analyses of elemental composition of stream sediments were compared with those found through such analyses made within the surrounding geological units—more specifically, Proterozoic crystalline, Tertiary volcanic, Quaternary loess, Neogene sediments, and Neogene coal. All the samples of the stream sediments examined revealed increased amounts of As, V, Ni, Cr, and Pb. Using the enrichment factor established on the basis of the regional geological background values proved that elevated levels of elements in stream sediments are not always the result of industrial contamination.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bábek, O., Grygar, T. M., Faměra, M., Hron, K., Nováková, T., & Sedláček, J. (2015). Geochemical background in polluted river sediments: How to separate the effects of sediment provenance and grain size with statistical rigour? Catena, 135, 240–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.07.003.
Blahová, J., Schandlová, L., Grabic, R., Fedorová, G., Randák, T., & Svobodová, Z. (2012). Assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination of the Bílina River (Czech Republic) using passive water samplers and fish biliary metabolites. Acta Veterinaria, 2011(80), 353–357. https://doi.org/10.2754/avb201180040353.
Bouška, V., & Pešek, J. (1999). Quality parameters of lignite of the North Bohemian Basin in the Czech Republic in comparison with the world average lignite. International Journal of Coal Geology, 40, 211–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-5162(98)00070-6.
Brügman, L. (1995). Metals in sediments and suspended matter of the Elbe River. Science of the Total Environment, 159, 53–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(94)04252-i.
Cajz, V., Vokurka, K., Balogh, K., Lang, M., & Ulrych, J. (1999). The České středohoří Mts.: Volcanostratigraphy and geochemistry. Geolines, 9, 21–28.
Caracciolo, L., Le Pera, E., Muto, F., & Perri, F. (2011). Sandstone petrology and mudstone geochemistry of the Peruc–Korycany Formation (Bohemian Cretaceous Basin, Czech Republic). International Geology Review, 53(9), 1003–1031. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206810903429011.
Doležalová Weismannová, H., Pavlovský, J., & Chovanec, P. (2015). Heavy metal contaminations of urban soils in Ostrava Czech Republic: assessment of metal pollution and using principal component analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research, 9, 683–696.
Famera, M., Babek, O., Matys Grygar, T., & Nováková, T. (2013). Distribution of heavy-metal contamination in regulated river-channel deposits: a magnetic susceptibility and grain-size approach; River Morava, Czech Republic. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 224, 1525–1542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1525-1.
Fojtík, S., Voroš, D., & Geršlová, E. (2018). Distribution of trace elements in the lower and upper benches of the main coal seam in the Most Basin. Geoscience Research Reports, 51(1), 43–45.
Grba, N., Neubauer, F., Šajnovič, A., Stojanovič, K., & Jovančičevič, B. (2015). Heavy metals in Neogene sedimentary rocks as a potential geogenic hazard for sediment, soil, and surface and groundwater contamination (eastern Posavina and the Lopare Basin, Bosnia and Herzegovina). Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society, 80(6), 827–838.
Jurajda, P., Adámek, Z., Janáč, M., & Valová, Z. (2010). Longitudal patterns in fish and macrozoobenthos assemblages reflect degradation of water quality and physical habitat in the Bilina river basin. Czech J. Anim. Sci., 3, 123–136.
Kaiglová, J., Jiřinec, P., Langhammer, J., Ingeduldová, E., Chalupová, D., Ferenčík, M., & Jánský, B. (2015a). Numerical modelling of heavily polluted fine-grained sediments remobilization in northern Czech Republic. Ecohydrology and Hydrobiology, 15, 111–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2015.02.001.
Kaiglová, J., Langhammer, J., Jiřinec, P., Janský, B., & Chalupová, D. (2015b). Numerical simulations of heavily polluted fine-grained sediment remobilization using 1D, 1D+ and 2D channel schematization. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(3), 115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4339-3.
Ketris, M., & Yudowich, Y. (2009). Estimations of clarkes for carbonaceous biolithes: world averages for trace element contents in black shales and coals. International Journal of Coal Geology, 78, 135–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2009.01.002.
Kohušová, K., Havel, L., Vlasák, P., & Tonika, J. (2011). A long-term survey of heavy metals and specific organic compounds in biofilms, sediments, and surface water in a heavily affected river in the Czech Republic. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 174, 555–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1478-4.
Kružíková, K., & Svobodová, Z. (2012). Assessment of mercury contamination in the Bílina River (Czech Republic) using indicator fish. Acta Veterinaria, 81, 63–68. https://doi.org/10.2754/avb201281010063.
Langedal, M. (1997). Dispersion of tailings in the Knabena—Kvina drainage basin, Norway, 1: Evaluation of overbank sediments as sampling medium for regional geochemical mapping. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 58, 2–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6742(96)00069-6.
Nováková, T., Matys Grygar, T., Kotková, K., Elznicová, J., Strnad, L., & Mihaljevič, M. (2015). Pollution assessment using local enrichment factors: the Berounka River (Czech Republic). Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16, 1081–1092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1315-z.
Orendt, C., Wolfram, G., Adámek, Z., Jurajda, P., & Schmitt-Jansen, M. (2012). The response of macroinvertebrate community taxa and functional groups to pollution along a heavily impacted river in Central Europe (Bilina River, Czech Republic). Biologia, 67, 180–199.
Pešek, J., & Sivek, M. (2016). Coal-bearing basins and coal deposits of the Czech Republic. Prague: Czech Geology Survey http://unicat.nalis.bg/Record/BAS.000521302#description.
Pešek, J., Bencko, V., Sýkorová, I., Vašíček, M., Michna, O., & Martinek, K. (2005). Some trace elements in coal of the Czech Republic, environment and health protection implications. Central European Journal of Public Health, 13, 153–158.
Pribylova, P., Klanova, J., & Holoubek, I. (2006). Contamination of the Czech aquatic environment by short and medium chain chlorinated paraffin’s. Environmental Pollution, 144(1), 248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.12.020.
Rieder, M., Crelling, J. C., Sustai, O., Drábek, M., Weiss, Z., & Klementová, M. (2007). Arsenic in iron disulfides in a brown coal from the North Bohemian Basin, Czech Republic. International Journal of Coal Geology, 71, 115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2006.07.003.
Rieuwerts, J., & Farago, M. (1996). Heavy metal pollution in the vicinity of a secondary lead smelter in the Czech Republic. Applied Geochemistry, 11, 17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/0883-2927(95)00050-X.
Sakan, S., Dević, G., Relić, D., Anđelković, I., Sakan, N., & Đorđević, D. (2014). Evaluation of sediment contamination with heavy metals: the importance of determining appropriate background content and suitable element for normalization. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 67, 97–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9633-4.
Schäfer, S., Buchmeier, G., Claus, E., Duester, L., Heininger, P., Körner, P., Mayer, P., Paschke, A., Rauert, C., Reifferscheid, G., Rüdel, H., Schlechtriem, C., Schröter-Kermani, C., Schudoma, D., Smedes, F., Steffen, D., & Vietoris, F. (2015). Bioaccumulation in aquatic systems: methodological approaches, monitoring and assessment. Environmental Sciences Europe, 27, 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-014-0036-z.
Sindern, S., Tremöhlen, M., Dsikowitzky, L., Gronen, L., Schwarzbauer, J., Siregar, T. H., Ariyani, F., & Irianto, H. E. (2016). Heavy metals in river and coast sediments of the Jakarta Bay region (Indonesia)—Geogenic versus anthropogenic sources. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 110(2, 30 September 2016), 624–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.003.
Singh, M., Müller, G., & Singh, I. B. (2003). Geogenic distribution and baseline concentration of heavy metals in sediments of the Ganges River, India. Journal of Geochemical Exploration., 80(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6742(03)00016-5.
Vilímek, V., & Raška, P. (2016). The Krušné Hory Mts.—The longest mountain range of the Czech Republic. In T. Pánek & J. Hradecký (Eds.), Landscapes and landforms of the Czech Republic. World Geomorphological Landscapes. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27537-6_10.
Voroš, D., Geršlová, E., Díaz-Somono, M., Sýkorová, I., Suárez-Ruizi, I., Havelcová, M., & Kuta, J. (2018). Distribution and mobility potential of trace elements in the main seam of the Most Coal Basin. International Journal of Coal Geology, 196, 139–147.
Vuković, D., Stankovič, S. J., Vukovič, Ž., & Jakkovič, K. (2014). Transport and storage of heavy metals in the Sava River Basin in Serbia. Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society, 79(3), 379–387.
Funding
The present paper was supported by the Ministry for the Environment of the Czech Republic, project ID: MZP-OOHPP-87/08/GP and the project entitled Centre for Texture Analysis (project ID: CZ.2.16/3.1.00/21538) implemented as part of the Operational Programme Prague - Competitiveness. The present paper was also financially supported by RECETOX (LM2015051 and CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_013/0001761) and CzechPolar2 (CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_013/0001708) research infrastructures and contributes to Masaryk University Project MUNI/A/1251/2017 and the long-term conceptual development research organisation RVO: 67985891.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vöröš, D., Geršlová, E., Nývlt, D. et al. Assessment of geogenic input into Bilina stream sediments (Czech Republic). Environ Monit Assess 191, 114 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7255-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7255-0