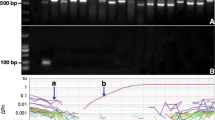
Abstract
Microalgal contamination in algal culture is a serious problem hampering the cultivation process, which can result in considerable economic and time losses. With the field of microalgal biotechnology on the rise, development of new tools for monitoring the cultures is of high importance. Here we present a case study of the detection of fast-growing green algae Chlorella vulgaris (as contaminant) in a diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum culture using various approaches. We prepared mixed cultures of C. vulgaris and P. tricornutum in different cell-to-cell ratios in the range from 1:103 to 1:107. We compared the sensitivity among microscopy, cultivation-based technique, PCR, and qPCR. The detection of C. vulgaris contamination using light microscopy failed in samples containing cell ratios <1:105. Our results confirmed PCR/qPCR to provide the most reliable and sensitive results, with detection sensitivity close to 75 cells/mL. The method was similarly sensitive in a pure C. vulgaris culture as well as in a mixed culture containing 107-times more P. tricornutum cells. A next-generation sequencing analysis revealed a positive discrimination of C. vulgaris during DNA extraction. The method of cultivation media exchange from sea water to fresh water, preferred by the Chlorella contaminant, demonstrated a presence of the contaminant with a sensitivity comparable to PCR approaches, albeit with a much longer detection time. The results suggest that a qPCR/PCR-based approach is the best choice for an early warning in the commercial culturing of microalgae. This method can be conveniently complemented with the substitution-cultivation method to test the proliferating potential of the contaminant.
Key points
• PCR-based protocol developed for detection of Chlorella cells.
• Synergy of various approaches shows deeper insight into a presence of contaminants.
• Positive/negative discrimination occurs during DNA extraction in mixed cultures.
• Newly developed assays ready to use as in diagnostics of contamination.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MM, Stanier RY (1968) Growth and division of some unicellular blue-green algae. J Gen Microbiol 51:199–202. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-51-2-199
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Barkia I, Saari N, Manning SR (2019) Microalgae for high-value products towards human health and nutrition. Mar Drugs 17:1–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050304
Bishop W, Zubeck MH (2012) Evaluation of microalgae for use as nutraceuticals and nutritional supplements. J Nutr Food Sci 02. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9600.1000147
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55:611–622. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797
Carney LT, Lane TW (2014) Parasites in algae mass culture. Front Microbiol 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00278
Church J, Hwang JH, Kim KT, McLean R, Oh YK, Nam B, Joo JC, Lee WH (2017) Effect of salt type and concentration on the growth and lipid content of Chlorella vulgaris in synthetic saline wastewater for biofuel production. Bioresour Technol 243:147–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.081
Costa JAV, de Morais MG (2013) An open pond system for microalgal cultivation. Biofuels from Algae:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-59558-4.00001-2
Dawidziuk A, Popiel D, Luboinska M, Grzebyk M, Wisniewski M, Koczyk G (2017) Assessing contamination of microalgal astaxanthin producer Haematococcus cultures with high-resolution melting curve analysis. J Appl Genet 58:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-016-0378-x
Day JG, Gong Y, Hu Q (2017) Microzooplanktonic grazers–A potentially devastating threat to the commercial success of microalgal mass culture. Algal Res 1:356–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2017.08.024
Day JG, Thomas NJ, Achilles-Day UEM, Leakey RJG (2012) Early detection of protozoan grazers in algal biofuel cultures. Bioresour Technol 114:715–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.03.015
Di Caprio F (2020) Methods to quantify biological contaminants in microalgae cultures. Algal Res 49:101943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2020.101943
Grivalský T, Ranglová K, da Câmara Manoel JA, Lakatos GE, Lhotský R, Masojídek J (2019) Development of thin-layer cascades for microalgae cultivation: milestones (review). Folia Microbiol (Praha) 64:603–614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-019-00739-7
Gurevich A, Saveliev V, Vyahhi N, Tesler G (2013) QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 29:1072–1075. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086
Havlik I, Reardon KF, Ünal M, Lindner P, Prediger A, Babitzky A, Beutel S, Scheper T (2013) Monitoring of microalgal cultivations with on-line, flow-through microscopy. Algal Res 2:253–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2013.04.001
Khan MI, Shin JH, Kim JD (2018) The promising future of microalgae: current status, challenges, and optimization of a sustainable and renewable industry for biofuels, feed, and other products. Microb Cell Factories 17:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-0879-x
Kralik P, Ricchi M (2017) A basic guide to real time PCR in microbial diagnostics: definitions, parameters, and everything. Front Microbiol 8:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00108
Letcher PM, Lopez S, Schmieder R, Lee PA, Behnke C, Powell MJ, McBride RC (2013) Characterization of Amoeboaphelidium protococcarum, an algal parasite new to the Cryptomycota isolated from an outdoor algal pond used for the production of biofuel. PLoS One 8:e56232. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056232
Metfies K, Berzano M, Mayer C, Roosken P, Gualerzi C, Medlin L, Muyzer G (2007) An optimized protocol for the identification of diatoms, flagellated algae and pathogenic protozoa with phylochips. Mol Ecol Notes 7:925–936. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01799.x
Oh SH, Jang CS (2020) Development and validation of a real-time PCR based assay to detect adulteration with corn in commercial turmeric powder products. Foods:9. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070882
Přibyl P, Cepák V, Kaštánek P, Zachleder V (2015) Elevated production of carotenoids by a new isolate of Scenedesmus sp. Algal Res 11:22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2015.05.020
Rai MP, Gautom T, Sharma N (2015) Effect of salinity, pH, light intensity on growth and lipid production of microalgae for bioenergy application. Online J Biol Sci 15:260–267. https://doi.org/10.3844/ojbsci.2015.260.267
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB (1979) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111:1–61. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-111-1-1
Starr RC, Zeikus JA (1993) UTEX—the culture collection of algae at the University of Texas at Austin. J Phycol 29:1–106
Staub R (1961) rnährungsphysiologisch-autökologische Untersuchungen an der planktischen Blaualge Oscillatoria rubescens DC. Schweiz Z Hydrol 23:82–198
Venancio HC, Cella H, Lopes RG, Derner RB (2020) Surface-to-volume ratio influence on the growth of Scenedesmus obliquus in a thin-layer cascade system. J Appl Phycol 32:821–829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02036-0
Wang H, Zhang W, Chen L, Wang J, Liu T (2013) The contamination and control of biological pollutants in mass cultivation of microalgae. Bioresour Technol 128:745–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.10.158
Wang Y, Castillo-Keller M, Eustance E, Sommerfeld M (2017) Early detection and quantification of zooplankton grazers in algal cultures by FlowCAM. Algal Res 21:98–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.11.012
Wrage J, Kleyner O, Rohn S, Kuballa J (2020) Development of a DNA-based detection method for cocos nucifera using TaqMan™ real-time PCR. Foods 9:332. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9030332
Wu T, Li L, Jiang X, Yang Y, Song Y, Chen L, Xu X, Shen Y, Gu Y (2019) Sequencing and comparative analysis of three Chlorella genomes provide insights into strain-specific adaptation to wastewater. Sci Rep 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45511-6
Zhu Z, Jiang J, Yun F (2020) Overcoming the biological contamination in microalgae and cyanobacteria mass cultivations for photosynthetic biofuel production. Molecules 25
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mr. Marek Romášek for corrections of English and Dr. Kateřina Holušová for sequencing library preparation and Illumina sequencing. Computational resources were supplied by the project “e-Infrastruktura CZ” (e-INFRA LM2018140) provided within the program Projects of Large Research, Development and Innovations Infrastructures.
Availability of data
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable
Funding
This work was supported by the Technology Agency of the Czech Republic programme National Centres of Competence: Support programme for applied research, experimental development and innovation (project ID TN01000048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design.TG, PP, JL, RH, and PH conceived and designed research. TG, AS, PP, JL, and RČ conducted experiments and analyzed the data. The first draft of the manuscript was written TG and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. PH revised and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Consent for publication
The authors give consent to the publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 390 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grivalský, T., Střížek, A., Přibyl, P. et al. Comparison of various approaches to detect algal culture contamination: a case study of Chlorella sp. contamination in a Phaeodactylum tricornutum culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 5189–5200 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11396-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11396-7