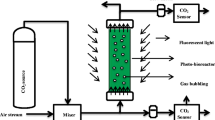
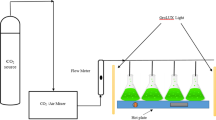
Abstract
This study investigated microalgal CO2 fixation at the CO2 concentration ranging from 5 to 40% and the CO2 loading rate of 14.4 to 57.6 L/L-d. Chlorella sp. (AG10133) was selected as the optimal strain for CO2 fixation among examined algal strains. The microalgal CO2 fixation was highly dependent on the CO2 loading rate as well as CO2 concentration. In batch culture, the highest CO2 fixation rate of 1.785 g/L-d was obtained at the CO2 concentration and the CO2 loading rate of 15% and 43.2 L/L-d, respectively. The high CO2 fixation performance was maintained at CO2 40% with the same CO2 loading rate. On the other hand, CO2 loading rate over 43.2 L/L-d at CO2 15% deteriorated CO2 fixation along with the decrease of microalgal growth. In continuous culture, the CO2 fixation rate of 2.25 g/L-d was achieved at the pseudo-steady state. The microalgal CO2 fixation would be suitable for high-strength CO2 gas stream such as biogas by providing proper CO2 loading rate.
Graphic Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
E-supplementary data of this work can be found in the online version of the paper.
References
Jang, K.Y.: Forecast of Domestic and Overseas Energy Market Outlook. POSCO Institute of Management, Busan (2017)
Renewable Energy 3020 Implementation Plan (proposal). Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. (2017). Accessed December 2017
Kerstin, H., Christian, H., Mattias, S., Josefin, J.: Biogas upgrading—technical review. Energiforsk 275 (2016).
Danish Technological Institute: Overview of Biogas Technologies for Production of Liquid Transport Fuels. Danish Technological Institute, Taastrup (2012)
Fredric, B., Tobias, P., Christian, H., Daniel, T.: Biogas upgrading—technology overview, comparison and perspectives for the future. Biofpr. 7(5), 499–511 (2013)
Kim, Y.S., Yoon, Y.M., Kim, C.H., Giersdorf, J.: Status of biogas technologies and policies in South Korea. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 16, 3430–3438 (2012)
Serejo, M.L., Posadas, E., Boncz, M.A., Blanco, S., García-Encina, P., Muñoz, R.: Influence of biogas flow rate on biomass composition during the optimization of biogas upgrading in microalgal-bacterial processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49, 3228–3236 (2015)
Bae, J.H., Yu, M.S., Ryu, D.S., Lee, J.K., Kim, C.K.: Waste Recycling: Biogas Production and Utilization. Dongwha Technology, Dongwha (2010)
Kim, Y.H., Kim, K.N., Ko, S.C.: Present and future of marine bioenergy, pp. 63–70. Korea Maritime University, Busan (2011)
Awe, O.W., Zhao, Y., Nzihou, A., Minh, D.P., Lyczko, N.: A review of biogas utilisation, purification and upgrading technologies. Waste Biomass Valor. 8, 267–283 (2017)
de Morais, M.G., Costa, J.: Biofixation of carbon dioxide by Spirulina Sp. and Scenedesmus Obliquus cultivated in a three-stage serial tubular photobioreactor. J. Biotechnol. 129(3), 439–445 (2007)
Yoon. Y.S.: 1996. Simultaneous removal of carbon dioxide from waste flue gas and nitrogen compounds from wastewater by algal cultivation. Master’s thesis, Pohang University
Kroumov, A.D., Módenes, A.N., Trigueros, D.E.G., Espinoza-Quiñones, F.R., Borba, C.E., Scheufele, F.B., Hinterholz, C.L.: A systems approach for CO2 fixation from flue gas by microalgae—theory review. Process Biochem. 51(11), 1817–1832 (2016)
Raven, J.A., Cockell, C.S., De La Rocha, C.L.: The evolution of inorganic carbon concentrating mechanisms in photosynthesis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 363(1504), 2641–2650 (2008)
Kim, T.: Industrial utility of microalgae, Tech news brief. Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information, Daejeon (2004)
Wang, B., Li, Y., Wu, N.: CO2 bio-mitigation using microalgae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 79(5), 707–718 (2008)
Ono, E., Cuello, J.L.: Selection of optimal microalgae species for CO2 sequestration. In: Proceedings of Second Annual Conference on Carbon Sequestration Alexandria. VA, Citeseer. (2003)
Judd, S.J., Momani, F.A.O.A., Znad, H., Ketife, A.M.D.A.: The cost benefit of algal technology for combined CO2 mitigation and nutrient abatement. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 71, 379–387 (2017)
de Souza, M.P., Hoeltz, M., Gressler, P.D., Benitez, L.B., Schneider, R.C.S.: Potential of microalgal bioproducts: general perspectives and main challenges. Waste Biomass Valor. 10, 2139–2156 (2019)
Apandi, N., Mohamed, R.M.S.R., Al-Gheethi, A., Gani, P., Ibrahim, A., Kassim, A.H.M.: Scenedesmus biomass productivity and nutrient removal from wet market wastewater, a bio-kinetic Study. Waste Biomass Valor. 10, 2783–2800 (2019)
Ho, S.H., Chen, C.Y., Lee, D.J., Chang, J.S.: Perspectives on microalgal CO2-emission mitigation systems—a review. Biotechnol. Adv. 29(2), 189–198 (2011)
Huy, M., Kumar, G., Kim, S.H.: Photoautotrophic cultivation of mixed microalgae consortia using various organic waste streams towards remediation and resource recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 247, 576–581 (2018)
Rodolfi, L., Chini, Z.G., Bassi, N., Padovani, G., Biondi, N., Bonini, G., Tredici, M.R.: Microalgae for oil: strain selection, induction of lipid synthesis and outdoor mass cultivation in a low-cost photobioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 102(1), 100–112 (2009)
Almomani, F.A., Örmeci, B.: Monitoring and measurement of microalgae using the first derivative of absorbance and comparison with chlorophyll extraction method. Environ. Monit. Assess. 190(2), 90 (2018)
Cossio, M.L.T., Giesen, L.F., Araya, G., Pérez-Cotapos, M.L.S., Vergara, R.L., Manca, M., Tohme, R.A., Holmberg, S.D., Bressmann, T., Lirio, D.R., Román, J.S., Solís, R.G., Thakur, S., Rao, S.N., Modelado, E.L., La, A.D.E., Durante, C., Tradición, U.N.A., En, M., Espejo, E.L., Fuentes, D.E.L.A.S., Yucatán, U.A., De, Lenin, C.M., Cian, L.F., Douglas, M.J., Plata, L., Héritier, F.: Manual on the production and use of life food for aquaculture. Uma ética Para Quantos. (1996).
American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA), and Water Environment Federation (WEF) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (20th Edition), United Book Press, Inc., Baltimore, Maryland (1998)
Lieve, M.L., Laurens, L.: Summative Mass Analysis of Algal Biomass—Integration of Analytical Procedures. Technical Report NREL/TP-5100–60943. (2013).
Lourenco, S.O., Barbarino, E., Lavin, P.L., Marquez, U.M.L., Aidar, E.: Distribution of intracellular nitrogen in marine microalgae: calculation of new nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors. Eur. J. Phycol. 39(1), 17–32 (2004)
Templeton, D.W., Laurens, L.M.L.: Nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors revisited for applications of microalgal biomass conversion to food, feed and fuel. Algal Res. 11, 359–367 (2015)
Burkhardt, S., Zondervan, I., Riebesell, U.: Effects of CO2 concentration on C:N: P ratio in marine phytoplankton: a species comparison. Limnol. Oceanogr. 44(3), 683–690 (1999)
Yang, Y., Gao, K.S.: Effects of CO2 concentrations on the freshwater microalgae, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Scenedesmus obli-quus (Chlorophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 15(5), 379–389 (2003)
Yoo, C., June, S.Y., Lee, J.Y., Ahn, C.Y., Oh, H.M.: Selection of microalgae for lipid production under high levels carbon dioxide. Bioresour. Technol. 101(1), 71–74 (2010)
Dragone, G., Fernandes, B.D., Abreu, A.P., Vicente, A.A., Teixeira, J.A.: Nutrient limitation as a strategy for increasing starch accumulation in microalgae. Appl. Energy. 88(10), 3331–3335 (2011)
Chiang, C.L., Lee, C.M., Chen, P.C.: Utilization of the cyanobacteria Anabaena sp. CH1 in biological carbon dioxide mitigation processes. Bioresour. Technol. 102(9), 5400–5405 (2011)
Zheng, M., Ji, X., He, Y., Li, Z., Wang, M., Chen, B., Huang, J.: Simultaneous fixation of carbon dioxide and purification of undiluted swine slurry by culturing Chlorella vulgaris MBFJNU-1. Algal Res. 47, 101866 (2020)
Ding, G.T., Yasin, N.H.M., Takriff, M.S., Kamarudin, K.F., Salihon, J., Yaakob, Z., Hakimi, N.I.N.M.: Phycoremediation of palm oil mill effluent (POME) and CO2 fixation by locally isolated microalgae: Chlorella sorokiniana UKM2, Coelastrella sp UKM4 and Chlorella pyrenoidosa UKM7. J. Water Process Eng. 35, 101202 (2020)
Ho, S.H., Chen, C.Y., Chang, J.S.: Effect of light intensity and nitrogen starvation on CO2 fixation and lipid/carbohydrate production of an indigenous microalga Scenedesmus obliquus CNW-N. Bioresour. Technol. 113, 244–252 (2012)
Ho, S.H., Kondo, A., Haseunuma, T., Chang, J.S.: Engineering strategies for improving the CO2 fixation and carbohydrate productivity of Scenedesmus obliquus CNW-N used for bioethanol fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 143, 163–171 (2013)
Almomani, F.A.: Assessment and modeling of microalgae growth considering the effects OF CO2, nutrients, dissolved organic carbon and solar irradiation. J. Environ. Manag. 247, 738–748 (2019)
Almomani, F., Al Ketife, A., Judd, S., Shurair, M., Bhosale, R.R., Znad, H., Tawalbeh, M.: Impact of CO2 concentration and ambient conditions on microalgal growth and nutrient removal from wastewater by a photobioreactor. Sci. Total Environ. 662, 662–671 (2019)
Chen, Y., Xu, C., Vaidyanathan, S.: Influence of gas management on biochemical conversion of CO2 by microalgae for biofuel production. Appl. Energy. 261, 114420 (2020)
Kim, Y.S., Park, H.I., Park, D.W.: Growth characteristics of spirulina platensis at different carbon dioxide concentration and flow rate. In: Proceedings of the 2003 Conference of the Korean Society of Environmental Engineers. 1357–1358 (2003).
Park, H.M., Lee, S.D.: The effect of CO2 fixation for microalgae based on CO2 concentration and flow rate. J. Wetlands Res. 20(4), 363–369 (2018)
Almomani, F., Judd, S., Bhosale, R.R., Shurair, M., Aljaml, K., Khraisheh, M.: Intergraded wastewater treatment and carbon bio-fixation from flue gases using Spirulina platensis and mixed algal culture. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 124, 240–250 (2019)
Znad, H., Ketife, A.M.D.A., Judd, S., AlMomani, F., Vuthaluru, H.B.: Bioremediation and nutrient removal from wastewater by Chlorella vulgaris. Ecol. Eng. 110, 1–7 (2018)
Metsoviti, M.N., Papapolymerou, G., Karapanagiotidis, I.T., Katsoulas, N.: Comparison of growth rate and nutrient content of five microalgae species cultivated in greenhouses. Plants. 8(8), 279 (2019)
AlMomani, F.A., Örmeci, B.: Performance of Chlorella Vulgaris, Neochloris Oleoabundans, and mixed indigenous microalgae for treatment of primary effluent, secondary effluent and centrate. Ecol. Eng. 95, 280–289 (2016)
Zheng, Y., Chi, Z., Lucker, B., Chen, S.: Two-stage heterotrophic and phototrophic culture strategy for algal biomass and lipid production. Bioresour. Technol. 103, 484–488 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the International Research & Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science & ICT (Grant Number: 2017K1A3A1A67015923).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J., Kumar, G., Bakonyi, P. et al. Comparative Evaluation of CO2 Fixation of Microalgae Strains at Various CO2 Aeration Conditions. Waste Biomass Valor 12, 2999–3007 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01226-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01226-8