Abstract
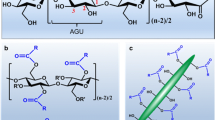
Applications of nanomaterials to biological systems have received increased interest in the past decades. In particular, bacterial cellulose nanofibers can be utilized in a broad range of applications. Biomaterials have been produced on large-scale with high reproducibility by an inspiring method such as molecular imprinting. Herein, for the first time, magnetic bacterial cellulose nanofibers are designed by the molecular imprinting method as a novel adsorbent for selective and efficient recognition of thymidine nucleoside. In this process, magnetic bacterial cellulose nanofibers are silanized with 3-(trimethoxysilyl) propyl methacrylate and further polymerized with a hydrophilic monomer for templating thymidine via metal chelate coordination. They are characterized by several methods and then applied for thymidine recognition to optimize the adsorption conditions. Hereby, the effecting factors are evaluated, and the highest adsorption capacity is obtained as 431.3 mg/g in pH 9.0 at 25 °C. The selectivity is assessed with competitor nucleosides and highly selective (4.13 and 3.80 times) adsorption of thymidine at the same concentration of other nucleosides (cytidine and uridine) is observed. After multiple adsorption–desorption experiments, the magnetic bacterial cellulose nanofibers also provided high reusability capacity. The present new work holds excellent potential for nucleoside recognition by integrating molecular imprinting with magnetic bacterial cellulose nanofibers.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albadarin AB, Collins MN, Naushad M, Shirazian S, Walker G, Mangwandi C (2017) Activated lignin-chitosan extruded blends for efficient adsorption of methylene blue. Chem Eng J 307:264–272
Arshad R, Rhouati A, Hayat A, Nawaz MH, Yameen MA, Mujahid A, Latif U (2020) MIP-based impedimetric sensor for detecting dengue fever biomarker. Appl Biochem Biotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03285-y
Baldikova E, Pospiskova K, Ladakis D, Kookos IK, Koutinas AA, Safarikova M, Safarik I (2017) Magnetically modified bacterial cellulose: a promising carrier for immobilization of affinity ligands, enzymes, and cells. Mater Sci Eng C 71:214–221
Boswell-Casteel RC, Johnson JM, Roe-Zurz Z, Duggan KD, Schmitz H, Hays FA (2018) Expression and purification of human and Saccharomyces cerevisiae equilibrative nucleoside transporters. Protein Express Purif 142:68–74
Breton F, Delpee R, Agrofoglio LA (2009) Molecular imprinting of AMP by an ionic noncovalent dual approach. J Sep Sci 32:3285–3291
Charreau H, Foresti ML, Vazquez A (2013) Nanocellulose patents trends: a comprehensive review on patents on cellulose nanocrystals, microfibrillated and bacterial cellulose. Recent Pat Nanotech 7:6–80
Chawla PR, Bajaj IB, Survase SA, Singhal RS (2009) Microbial cellulose: fermentative production and applications, fermentative production of microbial cellulose. Food Tech Biotechn 47:107–124
Clegg JR, Wagner AM, Shin SR, Hassan S, Khademhosseini A, Peppas N (2019) Modular fabrication of intelligent material-tissue interfaces for bioinspired and biomimetic device. Prog Mater Sci 106:100589
Denizli A, Garipcan B, Emir S, Patir S, Say R (2002) Heavy metal ion adsorption properties of methacrylamidocysteine-containing porous poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) chelating beads. Ads Sci Technol 20:607–617
Errasti-Murugarren E, Pastor-Anglada M (2010) Drug transporter pharmacogenetics in nucleoside-based therapies. Pharmacogenomics 11:809–841
Fan JP, Zhang PY, Yang XM, Zhang XH, Cao YH, Peng HL (2018) Preparation of a novel supermacroporous molecularly imprinted cryogel membrane with a specific ionic liquid for protein recognition and permselectivity. J Appl Polym 135(41):46740
Fathi F, Sharifi M, Jafari A, Kakavandi N, Kashanian S, Dolatabadi JEN, Rashidi MR (2019) Kinetic and thermodynamic insights into interaction of albumin with piperacillin: spectroscopic and molecular modeling approaches. J Mol Liquids 296:111770
Göktürk I, Tamahkar E, Yılmaz F, Denizli A (2018) Protein depletion with bacterial cellulose nanofibers. J Chromatogr B 1099:1–9
Greenhalf W et al (2014) Pancreatic cancer hENT1 expression and survival from gemcitabine in patients from the ESPAC-3 trial. J Natl Cancer I 106:1–10
Hao Z, Thomsen M, Postis VLG, Lesiuk A, Sharples D, Wang Y, Bartlam M, Goldman A (2016) A novel and fast purification method for nucleoside transporters. Front Mol Biosci 3:1–8
He H, Lu Q, Huang H, Xue F, Lin W, Zhou H, Wei W (2020) Biomass bagasse-based hyperbranched adsorbent for the complete removal of low-level Cr(VI). Cellulose 27:8121–8134
Ho YS (2004) Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions. Scientometr 59:171–177
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem Eng J 70:115–124
Hsu CL et al (2012) Equilibrative nucleoside transporter deficiency per turbs lysosome function and macrophage homeostasis. Science 335:89–92
Inci F, Karaaslan MG, Mataji-Kojouri A, Shah PA, Saylan Y, Zeng Y, Avadhani A, Sinclair R, Lau DTY, Demirci U (2020) Enhancing the nanoplasmonic signal by a nanoparticle sandwiching strategy to detect viruses. App Mater Today 20:100709
Iskierko Z, Sharma PS, Bartold K, Pietrzyk-Le A, Noworyta K, Kutner I (2016) Molecularly imprinted polymers for separating and sensing of macromolecular compounds and microorganisms. Biotechn Adv 34:30–46
Johnson ZL, Cheong CG, Lee SY (2012) Crystal structure of a concentrative nucleoside transporter from vibriocholerae at 2.4 A. Nature 483:489–493
Jordheim LP, Durantel D, Zoulim F, Dumontet C (2013) Advances in the development of nucleoside and nucleotide analogues for cancer and viral diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:447–464
Kim JH, Karpya VM, Biernacka JM, Nam HW, Lee MR, Preuss UW, Zill P, Yoon G, Colby C, Mrazek DA, Choi DS (2011) Functional role of the polymorphic 647 T/C variant of ENT1 (SLC29A1) and its association with alcohol withdrawal seizures. PLoS ONE 6:16331–16340
Knobloch B, Linert W, Sigel H (2005) Metal ion-binding properties of (N3)-deprotonated uridine, thymidine, and related pyrimidine nucleosides in aqueous solution. PNAS 102:7459–7464
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. J Am Chem Soc 38:2221–2295
Lim GW, Kang J, Ahmad AL, Chan CDJ (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymer layers using Navicula sp. frustule as core material for selective recognition of lysozyme. Chem Eng Res Des 101:2–14
Lombardo S, Thielemans W (2019) Thermodynamics of adsorption on nanocellulose surfaces. Cellulose 26:249–279
Lv XG, Yang JX, Feng C et al (2016) Bacterial cellulose-based biomimetic nanofibrous scaffold with muscle cells for hollow organ tissue engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2:19–29
Madhu S, Ramteke PW (2019) Cellulose as potential feedstock for cellulase enzyme production: versatility and properties of various cellulosic biomass-Part II. In: Srivastava M, Srivastava N, Ramteke P, Mishra P (eds) Approaches to enhance industrial production of fungal cellulases. Fungal biology. Springer, Cham, pp 117–125
Marques GO, Costa AL, Pereira C (2019) Gibbs free energy analysis for the NaOH (sodium-oxygen-hydrogen) thermochemical water splitting cycle. Int J Hydrog Energy 44(29):14536–14549
Massart R (1981) Preparation of aqueous magnetic liquids in alkaline and acidic media. IEEE Trans Magn 17(2):1247–1248
Mona S, Bajar S, Deepak B, Kiran B, Kaushik A (2019) Chapter 11: microbial cellulose—production and application. In: Grumezescu V, Grumezescu AM (eds) Materials for biomedical engineering. Absorbable polymers. Elsevier, pp 309–322
Nam HW, Hinton DJ, Kang NY, Kim T, Lee MR, Oliveros A, Adams C, Ruby CL, Choi DS (2013) Adenosine transporter ENT1 regulates the acquisition of goal-directed behavior and ethanol drinking through A2A receptor in the dorsomedial striatum. J Neurosci 33:4329–4338
Perçin I, Karakoç V, Akgöl S, Aksöz E, Denizli A (2012) Poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) based magnetic nanoparticles for plasmid DNA purification from Escherichia coli lysate. Mater Sci Eng C 32(5):1133–1140
Petridis L, Smith JC (2018) Molecular-level driving forces in lignocellulosic biomass deconstruction for bioenergy. Nature Rev Chem 2:382–389
Rehan S, Jaakola VP (2015) Expression, purification and functional characterization of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter subtype-1 (hENT1) protein from Sf9 insect cells. Protein Express Purif 114:99–107
Reiniati I, Hrymak AN, Margaritis A (2017) Recent developments in the production and applications of bacterial cellulose fibers and nanocrystals. Crit Rev Biotechnol 37:510–524
Rico-Yuste A, Carrasco S (2019) Molecularly imprinted polymer-based hybrid materials for the development of optical sensors. Polymers 11:1173
Rose JB, Coe IR (2008) Physiology of nucleoside transporters: back to the future. Physiol 23:41–48
Sadowska M, Wandelt B (2008) Molecularly imprinted thin polymeric film as a fluorescent sensor for nucleotides. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 486:203–212
Safarik I, Baldikova E, Prochazkova J, Safarikova M, Pospiskova K (2018a) Magnetically modified agricultural and food waste: preparation and application. J Agric Food Chem 66:2538–2552
Safarik I, Baldikova E, Safarikova M, Pospiskova K (2018b) Magnetically responsive textile for a new preconcentration procedure: magnetic textile solid phase extraction. J Ind Text 48:1–11
Safran V, Göktürk I, Derazshamshir A, Yılmaz F, Sağlam N, Denizli A (2019) Rapid sensing of Cu+2 in water and biological samples by sensitive molecularly imprinted based plasmonic biosensor. Microchem J 148:141–150
Saylan Y, Uzun L, Denizli A (2015) Alanine functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for reversible amyloglucosidase immobilization. Ind Eng Chem Res 54(1):454–461
Saylan Y, Tamahkar E, Denizli A (2017a) Recognition of lysozyme using surface imprinted bacterial cellulose nanofibers. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 28:1950–1965
Saylan Y, Yilmaz F, Özgür E, Derazshamshir A, Yavuz H, Denizli A (2017b) Molecular imprinting of macromolecules for sensor applications. Sensors 17(4):898
Saylan Y, Akgönüllü S, Yavuz H, Ünal S, Denizli A (2019) Molecularly imprinted polymer based sensors for medical applications. Sensors 19:1279
Saylan Y, Erdem Ö, Inci F, Denizli A (2020) Advances in biomimetic systems for molecular recognition and biosensing. Biomimetics 5(2):20
Shi L, Tang Y, Hao Y, He G, Gao R, Tang X (2016) Selective adsorption of protein by a high-efficiency Cu2+-cooperated magnetic imprinted nanomaterial. J Sep Sci 39(14):2876–2883
Skopp J (2009) Derivation of the Freundlich adsorption isotherm from kinetics. J Chem Educ 86:1341
Swartz HM, Bolton JR, Borg DC (1972) Biological applications of electron spin resonance. Wiley, New York
Tamahkar E, Bakhshpour M, Denizli A (2019) Molecularly imprinted composite bacterial cellulose nanofibers for antibiotic release. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 30:450–461
Tan IAW, Ahmad AL, Hameed BH (2008) Adsorption of basic dye on high-surface-area activated carbon prepared from coconut husk: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Hazard Mater 154:337–346
Valdés R, Elferich J, Shinde U, Landfear SM (2014) Identification of the intracellular gate for a member of the equilibrative nucleoside transporter (ENT) family. J Biol Chem 289:8799–8809
Wang X, Yu S, Liu W, Fu L, Wang Y, Li J, Chen L (2018) Molecular imprinting based hybrid ratiometric fluorescence sensor for the visual determination of bovine hemoglobin. ACS Sens 3:378–385
Xiang J, Li J, Zhang X, Ye Q, Xu J, Shen X (2014) Magnetic carbon nanofibers containing uniformly dispersed Fe/Co/Ni nanoparticles as stable and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. J Mater Chem A 2:16905–16914
Xu Z, Xu P, Chen Y, Liu J, Zhang Y, Lv Y, Luo J, Fang M, Zhang J, Wang J, Wang K, Wang X, Chen G (2015) ENT1 inhibition attenuates epileptic seizure severity via regulation of glutamatergic neurotransmission. NeuroMol Med 17:1–11
Ye S, Jiang L, Wu J, Su C, Huang C, Liu X, Shao W (2018) Flexible amoxicillin-grafted bacterial cellulose sponges for wound dressing: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:5862–5870
Young JD, Yao SY, Baldwin JM, Cass CE, Baldwin SA (2013) The human concentrative and equilibrative nucleoside transporter families, SLC28 and SLC29. Mol Aspescts Med 34:529–547
Yu Z, Bai B, Wang H, Ran X, Jin G, Sun J, Zhao C, Li M (2011) Morphology-tuning by changing the composition of a binary hydrogel comprising thymidine and melamine. Mater Sci Eng C 31:880–884
Zhang Z, Hu YF, Zhang HB, Luo LJ, Yao SZ (2010) Electrochemical layer-by-layer modified imprinted sensor based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes and sol–gel materials for sensitive determination of thymidine. J Electroanal Chem 644:7–12
Zhang Y, Huang S, Qian C, Wu Q, He J (2016) Preparation of cinchonine molecularly imprinted photonic crystal film and its specific recognition and optical responsive properties. J Appl Polym 133(11):43191
Zhao X, Han W, Jiang Y, Zhao C, Ji X, Kong F, Xu W, Zhang X (2019) A honeycomb-like paper-based thermoelectric generator based on a Bi2Te3/bacterial cellulose nanofiber coating. Nanoscale 11:17725–17735
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Hacettepe University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit (FHD-2018-16349). The authors thank Dr. Apostolis Koutinas (Agricultural University of Athens, Greece) for providing bacterial cellulose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saylan, Y., Göktürk, l., Pospiskova, K. et al. Magnetic bacterial cellulose nanofibers for nucleoside recognition. Cellulose 27, 9479–9492 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03425-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03425-x