Abstract
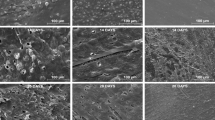
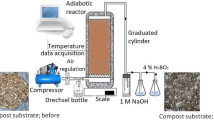
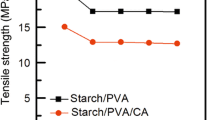
In this work, biodegradable aliphatic polyester blends of polycaprolactone and polylactide were melted and blended with a natural and biodegradable thermoplastic starch (TPS). The TPS employed in this study was obtained by plasticization of isolated wheat starch using glycerol as plasticizer. Morphology as well as thermal properties of the blends was investigated, and water vapor permeability as a barrier property was also monitored. The biodegradability of the biodegradable blends was performed by a composting process on laboratory scale. The composting process was conducted in an adiabatic closed reactor for 21 days and during the composting process, the temperature, pH value, % moisture and volatile matter and evolved CO2 were monitored. Biodegradation of the blends was determined by weight loss, as well as monitoring of morphological surface change. The thermophilic phase prevailed in the composting process, indicating intensive biodegradation of substrate as well as biodegradation of investigated ternary blends. Since microorganisms use starch as a carbon source, addition of TPS causes considerable acceleration of biodegradation of ternary blends due to higher water vapor permeability as a result of the hydrophilic nature of starch. The thermoplastic starch was first degraded within the blend, which was facilitated access to the microorganisms of other ingredients in the blend, encouraging the biodegradation of other components.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul KHPS, Tye YY, Saurabh CK, Leh CP, Lai TK, Chong EWN, Fazita NMR, Mohd HJ, Banerjee A, Syakir MI (2017) Biodegradable polymer films from seaweed polysaccharides: a review on cellulose as a reinforcement material. eXPRESS Polym Lett 11:244–265. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2017.26
Ačkar Ð, Babić J, Šubarić D, Kopjar M, Miličević B (2010) Isolation of starch from two wheat varieties and their modification with epichlorohydrin. Carbohydr Polym 81:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.01.058
Antosik AK, Wilpiszewska K (2018) Natural composites based on polysaccharide derivatives: preparation and physicochemical properties. Chem Pap 72:3215–3218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0550-3
Auras R, Harte B, Selke SE (2004) An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol Biosci 4:835–864. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.200400043
Austrian Standards Institute (1986) Austrian standard: analytical methods and quality control for waste compost. ÖNORM S 2023, Vienna
Averous L, Moro L, Dole P, Fringant C (2000) Properties of thermoplastic blends: starch-polycaprolactone. Polymer 41:4157–4167. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(99)00636-9
Bota J, Lj Kratofil Krehula, Katančić Z, Brozović M, Hrnjak-Murgić Z (2017) Surface characteristics and enhancement of water vapor properties of paperboard coated with polycaprolactone nanocomposites. J Adhes Sci Technol 31:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/01694243.2016.1218313
Briški F, Kopčić N, Ćosić I, Kučić D, Vuković M (2012) Biodegradation of tobacco waste by composting: genetic identification of nicotine-degrading bacteria and kinetic analysis of transformations in leachate. Chem Pap 66:1103–1110. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-012-0234-3
Brody AL (2005) Commercial uses of active food packaging and modified atmosphere packaging systems. In: Han JH (ed) Innovations in food packaging. Elsevier Science, Oxford, pp 457–474
Broz ME, Vander HDL, Washburn NR (2003) Structure and mechanical properties of poly(d, l-lactic acid)/poly(ϵ-caprolactone) blends. Biomaterials 24:4181–4190. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00314-4
Carbonell-Verdu Ferri JM, Dominici F, Boronat T, Sanchez-Nacher L, Balart R, Torre L (2018) Manufacturing and compatibilization of PLA/PBAT binary blends by cottonseed oil-based derivatives. eXPRESS Polym Lett 12:808–823. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2018.69
Carmona VB, Correˆ AC, Marconcini JM, Capparelli Mattoso LH (2015) Properties of a biodegradable ternary blend of thermoplastic starch (TPS), poly(e-caprolactone) (PCL) and poly(lactic acid) (PLA). J Polym Environ 23:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-014-0666-7
Carvalho AJF, Zambon MD, Curvelo AAS, Gandini A (2003) Size exclusion chromatography characterization of thermoplastic starch composites 1. Influence of plasticizer and fibre content. Polym Degrad Stab 79:133–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-3910(02)00265-3
Chen L, Qiu X, Xie Z, Hong Z, Sun J, Chen X, Jing X (2006) Poly(l-lactide)/starch blends compatibilized with poly(l-lactide)-g-starch copolymer. Carbohydr Polym 65:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.12.029
Crescenzi V, ManziniG Calzolari G, Borri C (1972) Thermodynamics of fusion of poly-β-propiolactone and poly-ϵ-caprolactone. Comparative analysis of the melting of aliphatic polylactone and polyester chains. Eur Polym J 8:449–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-3057(72)90109-7
Curvelo AAS, Carvalho AJF, Agnelli JAM (2001) Thermoplastic starch-cellulosic fibers composites: preliminary results. Carbohydr Polym 45:183–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(00)00314-3
Davoodi S, Oliaei E, Davachi SM, Hejazi I, Seyfi J, Be S, Ebrahimi H (2016) Preparation and characterization of interface-modified PLA/starch/PCL ternary blends using PLLA/triclosan antibacterial nanoparticles for medical applications. RSC Adv. 6:39870–39882. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra07667j
Feng F, Ye L (2011) Morphologies and mechanical properties of polylactide/thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer blends. J Appl Polym Sci 119:2778–2783. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.32863
Ferreira ARV, Alves VD, Coelhoso IM (2016) Polysaccharide-based membranes in food packaging applications. Membranes (Basel) 6:22–39. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes6020022
Ferri JM, Fenollar O, Jorda-Vilaplana A, García-Sanoguera D, Balart R (2016) Effect of miscibility on mechanical and thermal properties of poly(lactic acid)/polycaprolactone blends. Polym Int 65:453–463. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.5079
Fortelny I, Slouf M, Sikora A, Hlavata D, Hasova V, Mikesova J, Jacob C (2006) The effect of the architecture and concentration of styrene-butadiene compatibilizers on the morphology of polystyrene/low-density polyethylene blends. J Appl Polym Sci 100:2803–2816. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.23731
Fox PG, Fuller KNG (1971) Thermal mechanism for craze formation in brittle amorphous polymers. Nat Phys Sci 234:13–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/physci234013a0
Garcia-Campo MJ, Quiles-Carrillo L, Masia J, ReigPérez MJ, Montanes N, Balart R (2017) Environmentally friendly compatibilizers from soybean oil for ternary blends of poly(lactic acid)-PLA, poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-PCL and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-PHB. Materials 10:1339/1–1339/19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111339
Ghasemlou M, Aliheidari N, Fahmi R, Shojaee-Aliabadi S, Keshavarz B, Cran MJ, Khaksar R (2013) Physical, mechanical and barrier properties of corn starch films incorporated with plant essential oils. Carbohydr Polym 98:1117–1126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.07.026
Gumede TP, Luyt AS, Müller AJ (2018) Review on PCL, PBS, and PCL/PBS blends containing carbon nanotubes. eXPRESS Polym Lett 12:505–529. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2018.43
Hosseini SF, Rezaei M, Zandi M, Ghavi FF (2013) Preparation and functional properties of fish gelatin–chitosan blend edible films. Food Chem 136:1490–1495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.081
Huang SJ (2005) Poly(lactic acid) and copolyesters. In: Bastioli C (ed) Handbook of biodegradable polymers. Rapra Technology Litmited, Shawbury, pp 287–297
Huang M, Yu J, Ma X (2005) Ethanolamine as a novel plasticiser for thermoplastic starch. Polym Degrad Stab 90:501–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2005.04.005
Jayasekara R, Harding I, Bowater I, Lonergan G (2005) Biodegradability of a selected range of polymers and polymer blends and standard methods for assessment of biodegradation. J Polym Environ 13:231–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-005-4758-2
Jiang W, Qiao X, Sun K (2006) Mechanical and thermal properties of thermoplastic acetylated starch/poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) blends. Carbohydr Polym 65:139–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.12.038
Kolthoff IM, Sandel EB (1951) Inorganic quantitative analysis. Školska knjiga, Zagreb, pp 347–352
Kostakova EK, Meszaros L, Maskova G, Blazkova L, Turcsan T, Lukas D (2017) Crystallinity of electrospun and centrifugal spun polycaprolactone fibers: a comparative study. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8952390
Kučić D, Kopčić N, Briški F (2013) Zeolite and potting soil sorption of CO2 and NH3 evolved during co-composting of grape and tobacco waste. Chem Pap 67:1172–1180. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-013-0322-z
Labet M, Thielemans W (2009) Synthesis of polycaprolactone: a review. Chem Soc Rev 38:3484–3504. https://doi.org/10.1039/b820162p
Lu X, Zhao J, Yang X, Xiao P (2017) Morphology and properties of biodegradable poly (lactic acid)/poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends with different viscosity ratio. Polym Test 60:58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2017.03.008
Mittal V, Akhtar T, Matsko N (2015) Mechanical, thermal, rheological and morphological properties of binary and ternary blends of PLA, TPS and PCL. Macromol Mater Eng 300:423–435. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201400332
Musioł M, Sikorska W, Janeczek H, Wałach W, Hercog A, Johnston B, Rydz J, Rydz J (2018) (Bio)degradable polymeric materials for a sustainable future—part 1. Organic recycling of PLA/PBAT blends in the form of prototype packages with long shelf-life. Waste Manag 77:447–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.04.030
Nair LS, Laurencin CT (2007) Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog Polym Sci 32:762–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2007.05.017
Neto BAM, Fornari Junior CCM, da Silva EGP, Franco M, Reis NS, Bonomo RCF, de Almeida PF, Pontes KV (2017) Biodegradable thermoplastic starch of peach palm (Bactris gasipaes Kunth) fruit: production and characterisation. Int J Food Prop 20:S2429–S2440. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2017.1372472
Ortega-Toro R, Morey I, Talens P, Chiralt A (2015) Active bilayer films of thermoplastic starch and polycaprolactone obtained by compression molding. Carbohydr Polym 127:282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.03.080
Palsikowski PA, Kuchnier CN, Pinheiro IF, Morales AR (2018) Biodegradation in soil of PLA/PBAT blends compatibilized with chain extender. J Polym Environ 26:330–334
Perotti GF, Kijchavengkul T, Auras RA, Constantino VRL (2017) Nanocomposites based on cassava starch and chitosan. Modified clay: physico-mechanical properties and biodegradability in simulated compost soil. J Braz Chem Soc 28:649–658. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20160213
Plichta A, Lisowska P, Kundys A, Zychewicz A, Debowski M, Florjanczyk Z (2014) Chemical recycling of poly(lactic acid) via controlled degradation with protic (macro)molecules. Polym Degrad Stab 108:288–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.03.006
Rhim J-W, Lee JH, Ng Perry KW (2007) Mechanical and barrier of biodegradable soy protein isolate-based films coated with polylactic acid. LWT Food Sci Technol 40:232–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2005.10.002
Sarazin P, Li G, Orts WJ, Favis BD (2008) Binary and ternary blends of polylactide, polycaprolactone and thermoplastic starch. Polymer 49:599–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2007.11.029
Selke SE (2000) Plastics recycling and biodegradable plastics. In: Harper CA (ed) Modern plastics handbook. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 12.1–12.108
Selke SE, Culter JD, Hernandez RJ (2004) Plastics packaging: properties, processing, applications, and regulations. Hanser, Cincinnati, pp 448–467
Shogren R (1997) Water vapor permeability of biodegradable polymers. J Environ Polym Degrad 5:91–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02763592
Siracusa V, Rocculi P, Romani S, Rosa MD (2008) Biodegradable polymers for food packaging: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 19:634–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2008.07.003
Slouf M, Kolarik J, Fambri L (2004) Phase morphology of PP/COC blends. J Appl Polym Sci 91:253–259. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.13253
Sorrentino A, Gorrasi G, Vittoria V (2007) Potential perspectives of bio-nanocomposites for food packaging applications. Trends Food Sci Technol 18:84–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2006.09.004
Su J, Chen L, Li L (2012) Characterization of polycaprolactone and starch blends for potential application within the biomaterials field. Afr J Biotechnol 11:694–701. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.251
Sun H, Xiao A, Yu B, Bhat G, Zhu F (2017) Effect of PCL and compatibilizer on the tensile and barrier properties of PLA/PCL films. Polymer (Korea) 4:181–188. https://doi.org/10.7317/pk.2017.41.2.181
Taggort P (2004) Starch as an ingredient: manufacture and applications. In: Eliasson AC (ed) Starch in food: structure, function and applications. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, pp 363–392
Thakur VK, Thakur MK (2016) Handbook of sustainable polymers: processing and applications. Pan Stanford Publishing, Singapore
Tumwesigye KS, Oliveira JC, Sousa-Gallagher MJ (2016) New sustainable approach to reduce cassava borne environmental waste and develop biodegradable materials for food packaging applications. Food Packag Shelf Life 7:8–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2015.12.001
Vertuccio L, Gorrasi G, Sorrentino A, Vittoria V (2009) Nano clay reinforced PCL/starch blends obtained by high energy ball milling. Carbohydr Polym 75:172–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.07.020
Yu L, Dean K, Li L (2006) Polymer blends and composites from renewable resources. Prog Polym Sci 31:576–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2006.03.002
Zembouai I, Kaci M, Bruzaud S, Benhamida A, Corre Y-M, Grohens Y (2013) A study of morphological, thermal, rheological and barrier properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/polylactide blends prepared by melt mixing. Polym Test 32:842–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2013.04.004
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the University of Zagreb, Croatia (Grant no. 110001/2013). Electron microscopy at the Institute of Macromolecular Chemistry was supported by projects TE01020118 (Technology Agency of the CR) and POLYMAT LO1507 (Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the CR, program NPU I).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bulatović, V.O., Grgić, D.K., Slouf, M. et al. Biodegradability of blends based on aliphatic polyester and thermoplastic starch. Chem. Pap. 73, 1121–1134 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0663-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0663-8