Abstract
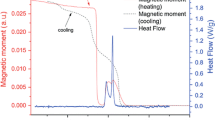
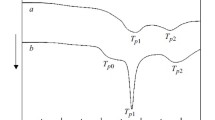
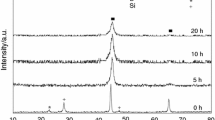
Thermal treatment of Fe40Ni40B12Si8 amorphous alloy leads to crystallization of various Fe and Ni-containing phases and their recrystallization, affecting the functional properties of the alloy. Kinetics of multistep crystallization of Fe40Ni40B12Si8 amorphous alloy and influence of thermally induced microstructural transformations on magnetic moment of the alloy were studied by means of structural examination, thermal analysis and thermomagnetic measurements. Temperature regions of growth and loss of magnetic moment of the alloy were correlated with the microstructural changes. Curie temperatures of the alloy in fully amorphous and fully crystallized form were observed at 620 and 910 K, respectively. Detailed kinetic study including deconvolution of the complex exothermic DTA peaks yielded Arrhenius parameters and kinetic model of individual crystallization steps, which reflect the nature of the studied processes and the alloy chemical composition. The obtained parameters and kinetic models can be used for kinetic predictions of thermal stability and functionality of the alloy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suryanarayana C, Inoue A. Metallic glasses. In: Giuseppe Bellussi, Matthias Bohnet, James Bus, Karlheinz Drauz, Helmut Greim, Klaus-Peter Jäckel, Uwe Karst, Axel Kleemann, Gerhard Kreysa, Trevor Laird, Willi Meier, Eckhard Ottow, Michael Röper, Japie Scholtz, Kai Sundmacher, Roland Ulber, Ulrich Wietelmann, editors. Ullmann’s encyclopedia of industrial chemistry. 7th edn. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA; 2012.
Suryanarayana C, Inoue A. Iron-based bulk metallic glasses. Int Mater Rev. 2013;58:131–66.
Minić DG, Blagojević VA, Mihajlović LE, Ćosović VR, Minić DM. Kinetics and mechanism of structural transformations of Fe75Ni2Si8B13C2 amorphous alloy induced by thermal treatment. Thermochim Acta. 2011;519:83–9.
Mitra A, Rao V, Pramanik S, Mohanty ON. Crystallization study of amorphous Fe40Ni40B20 by electrical resistivity measurements. J Mater Sci. 1992;27:5863–8.
Zhukov A, Churyukanova M, Kaloshkin S, Semenkova V, Gudoshnikov S, Ipatov M, Talaat A, Blanco JM, Zhukova V. Effect of annealing on magnetic properties and magnetostriction coefficient of Fe-Ni-based amorphous microwires. J Alloy Compd. 2015;651:718–23.
Sun BR, Xin SW, Shen TD. Low-temperature magnetization and magnetic exchange interactions in Fe40Ni40P14B6 bulk metallic glasses. J Magn Magn Mater. 2017;429:276–80.
Zhang L, Ma XH, Li Q, Zhang J, Dong Y, Chang C. Preparation and properties of Fe80-xNixP14B6 bulk metallic glasses. J Alloy Compd. 2014;608:79–84.
Aronhime N, DeGeorge V, Keylin V, Ohodnicki P, McHenry ME. The effects of strain-annealing on tuning permeability and lowering losses in Fe-Ni-based metal amorphous nanocomposites. JOM. 2017;69:2164–70.
Hasegawa R. Applications of amorphous magnetic alloys in electronic devices. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2001;287:405–12.
Gleiter H. Nanocrystalline materials. Prog Mater Sci. 1989;33:223–315.
Du SW, Ramanujan RV. Crystallization and magnetic properties of Fe40Ni38B18Mo4 amorphous alloy. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2005;351:3105–13.
Zaluska A, Matyja H. Differences in crystallization of Fe-Ni-based metallic glasses caused by changes in heating conditions. Mat Sci Eng. 1988;97:347–50.
Vyazovkin S. Modern isoconversional kinetics: from misconceptions to advances, handbook of thermal analysis and calorimetry, vol. 6. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2018. p. 131–72.
Svoboda R, Málek J. Crystallization mechanisms occurring in the Se–Te glassy system. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119:155–66.
Szepcsik B, Pukánszky B. Separation and kinetic analysis of the thermo-oxidative reactions of polyacrylonitrile upon heat treatment. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;133:1371–8.
Hazzat ME, Sifou A, Arsalane S, Hamidi AE. Novel approach to thermal degradation kinetics of gypsum: application of peak deconvolution and Model-Free isoconversional method. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;140:657–71.
Olejnik A, Gosz K, Piszczyk Ł. Kinetics of cross-linking processes of fast-curing polyurethane system. Thermochim Acta. 2020;683:178435.
Shilyaeva Y, Volovlikova O, Smirnov D, Volkova A, Sysa A, Mikhailova M, Gavrilov S. Thermal and kinetic analyses of silicide formation at nanostructured Si/Ni interface. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;138:2339–45.
Minić DM, Blagojević VA, Minić DM, David B, Pizúrová N, Žák T. Nanocrystal growth in thermally treated Fe75Ni2Si8B13C2 amorphous alloy. Metall Mater Trans A. 2012;43A:3062–9.
Tomić P, Davidović M. The study of relaxational properties and crystallization of the metallic glass Fe80Sil0B10. J Non-Cryst Solids. 1996;204:32–7.
Kaloshkin SD, Tomilin IA. The crystallization kinetics of amorphous alloys. Thermochim Acta. 1996;280–1:303–17.
Wei G, Cantor B. The effect of heat treatment and surface treatment on the crystallisation behaviour of amorphous Fe40Ni40B20. Acta Metall. 1989;37:3409–24.
Pradell T, Sunol JJ, Clavaguera N, Clavaguera-Mora MT. Crystallization behaviour of Fe40Ni40SixP20−x (x = 6, 10, 14) amorphous alloys. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2000;276:113–21.
Vasić MM, Roupcová P, Pizúrová N, Stevanović S, Blagojević VA, Žák T, Minić DM. Thermally induced structural transformations of Fe40Ni40P14B6 amorphous alloy. Metall Mater Trans A. 2016;47A:260–7.
Ma H, Wang W, Zhang J, Li G, Cao C, Zhang H. Crystallization and corrosion resistance of (Fe0.78Si0.09B0.13)100−xNix (x=0, 2 and 5) glassy alloys. J Mater Sci Technol. 2011;27:1169–77.
Long ZL, Chang CT, Ding YH, Shao Y, Zhang P, Shen BL, Inoue A. Corrosion behavior of Fe-based ferromagnetic (Fe, Ni)–B–Si–Nb bulk glassy alloys in aqueous electrolytes. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2008;354:4609–13.
Li Q. Formation of ferromagnetic bulk amorphous Fe40Ni40P14B6 alloys. Mater Lett. 2006;60:3113–7.
Gobran NK, Danial MM, Kamel R. Kinetics of the amorphous-crystalline transition in the metallic glass Fe40Ni40B20. Phys Stat Sol. 1984;82:63–6.
Raja VS, Ranganathan KS. Microstructural and kinetic aspects of devitrification of Fe40Ni40B20 metallic glass. J Mater Sci. 1990;25:4667–77.
Gu B, Liu F, Chen YZ, Yiang YH, Ma YZ. Structural modification and transformation kinetics: crystallization of amorphous Fe40Ni40P14B6 eutectic alloy. J Mater Sci. 2014;49:842–57.
Vasić MM, Blagojević VA, Begović NN, Žák T, Pavlović VB, Minć DM. Thermally induced crystallization of amorphous Fe40Ni40P14B6 alloy. Thermochim Acta. 2015;614:129–36.
Vasić MM, Žák T, Pizúrová N, Simatović IS, Minić DM. Influence of thermal treatment on microstructure and corrosion behavior of amorphous Fe40Ni40B12Si8 alloy. Metall Mater Trans. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-020-06079-3.
http://www.crystallography.net. Accessed 1 Sept 2014 and 6 Mar 2017
ICSD Inorganic Crystals Structure Database, Release 2014/2, FIZ Karlsruhe, Eggenstein-Leopoldshafen, Germany.
Lutterotti L. Total pattern fitting for the combined size-strain-stress-texture determination in thin film diffraction. Nucl Instrum Meth B. 2010;268:334–40.
Žák T, Jirásková Y. CONFIT: Mössbauer spectra fitting program. Surf Interface Anal. 2006;38:710–4.
Vyazovkin S, Burnham AK, Criado JM, Pérez-Maqueda LA, Popescu C, Sbirrazzuoli N. ICTAC kinetics committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim Acta. 2011;520:1–19.
Málek J. Kinetic analysis of crystallization processes in amorphous materials. Thermochim Acta. 2000;355:239–53.
Šesták J, Berggren G. Study of the kinetics of the mechanism of solid-state reactions at increasing temperatures. Thermochim Acta. 1971;3:1–12.
Becker JJ, Luborsky FE, Walter JL. Magnetic moments and Curie temperatures of (Fe, Ni)80(P, B)20 amorphous alloys. IEEE T Magn. 1977;13:988–91.
Minić DM, Blagojević VA, Maričić AM, Žák T, Minić DM. Influence of structural transformations on functional properties of Fe75Ni2Si8B13C2 amorphous alloy. Mater Chem Phys. 2012;134:111–5.
Minić DM, Minić DM, Žák T, Roupcová P, David B. Structural transformations of Fe81B13Si4C2 amorphous alloy induced by heating. J Magn Magn Mater. 2011;323:400–4.
Dahal A, Gunasekera J, Harringer L, Singh DK, Singh DJ. Metallic nickel silicides: Experiments and theory for NiSi and first principles calculations for other phases. J Alloy Compd. 2016;672:110–6.
Chiriac H, Lupu N. New bulk amorphous magnetic materials. Phys B. 2001;299:293–301.
Neamtu BV, Chicinas HF, Marinca TF, Isnard O, Chicinas I. Preparation and characterisation of Co–Fe–Ni–M-Si–B (M = Zr, Ti) amorphous powders by wet mechanical alloying. J Alloy Compd. 2016;673:80–5.
Chiriac H, Pletea M, Hristoforou E. Fe-based amorphous thin film as a magnetoelastic sensor material. Sensor Actuat. 2000;81:166–9.
Ramasamy S, Lundgren L, Ganesan K, Narayanasamy A. Thermomagnetic and crystallisation behaviour of amorphous Fe95−xW5Bx alloys. J Phys F Met Phys. 1987;17:753–65.
Kissinger HE. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem. 1957;29:1702–6.
Ortega A. A simple and precise linear integral method for isoconversional data. Thermochim Acta. 2008;474:81–6.
Ozawa T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1965;38:1881–6.
Flynn JH, Wall LA. A quick, direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data. Polym Lett. 1966;4:323–8.
Akahira T, Sunose T. Trans. Joint Convention of Four Electrical Institutes, paper no. 246, 1969 research report, Chiba Institute of Technology. J Sci Educ Technol. 1971;16:22–31.
Vogel H, Heimendahl MV. The effect of pre-annealing on the subsequent crystallization in the metallic glasses Fe–Ni–P–B and Fe–Ni–Cr–P–B using transmission electron microscopy. Mat Sci Eng. 1983;57:171–9.
Scott MG. The crystallization kinetics of Fe–Ni based metallic glasses. J Mater Sci. 1978;13:291–6.
Wu Y, Hui XD, Lu ZP, Liu ZY, Liang L, Chen GL. Effects of metalloid elements on the glass-forming ability of Fe-based alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2009;467:187–90.
Criado JM, Malek J, Ortega A. Applicability of the master plots in kinetic analysis of non-isothermal data. Thermochim Acta. 1989;147:377–85.
Perez-Maqueda LA, Criado JM, Gotor FJ, Malék J. Advantages of combined kinetic analysis of experimental data obtained under any heating profile. J Phys Chem A. 2002;106:2862–8.
Vyazovkin S. Model-free kinetics—staying free of multiplying entities without necessity. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;83:45–51.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (contract No. 451-03-68/2020-14/200146) and by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic under the projects CEITEC 2020 (LQ1601), and m-IPMinfra (CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_013/0001823). The authors want to sincerely thank Prof. Nikola Cvjetićanin (Faculty of Physical Chemistry, University of Belgrade, Serbia) for performing DTA measurements and Ing. Pavla Roupcová, PhD (Institute of Physics of Materials AS CR, Brno, Czech Republic) for performing XRD measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasić, M.M., Žák, T. & Minić, D.M. Kinetics and influence of thermally induced crystallization of Fe,Ni-containing phases on thermomagnetic properties of Fe40Ni40B12Si8 amorphous alloy. J Therm Anal Calorim 147, 3543–3551 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-10819-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-10819-x