Abstract
Geotherms of four crustal profiles across the Variscan orogen in SW Poland have been constructed to better understand the variation in thermal state of the region. Seismic and drilling data as well as rock sequences in exposed parts of the orogen were used for Wilcza Góra (Sudetic Block), Polkowice–Rudna (Middle Odra Horst), Święciechowa (Wolsztyn–Leszno Horst) and Września (Szczecin–Miechów Synclinorium within TESZ) profiles. The palaeoclimate-corrected surface heat flow map and the heat-production calculations based on literature data enabled the construction of geotherms and estimation of Moho heat flow. Exception is the Polkowice–Rudna profile, where the surface heat flow was calculated using temperature measurements in underground copper mines, and K, U and Th contents and density/heat conductivity measurements in rocks drilled in the Middle Odra Horst were used to calculate geotherm. The basaltic lava migration through the lithospheric mantle and its effect on crustal geotherm in Wilcza Góra (area of Cenozoic alkaline volcanism at ca. 30–18 Ma) was shown to increase slightly both current surface and current Moho heat flow (by ca. 4 mW/m2). The presented approach couples geological and geophysical information and thus differs from standard purely geophysical assessment of lithosphere thermal state. It shows that surface heat flow is enlarged to 84 mW/m2 by granitic plutons in the upper crust in the Lubin–Polkowice site. Heat flow on the Moho varies from 28 to 34 mW/m2 in sites located in the Sudetic- /Fore-Sudetic Blocks, Middle Odra Horst and Wolsztyn–Leszno Horst. Locally it may slightly increase because of extraneous heat input by Cenozoic basaltic volcanism, but the values close to 30 mW/m2 are specific for mantle root of Saxothuringian Zone in SW Poland. Mantle heat flow is 36 mW/m2 in Września site and supposedly is a manifestation of different nature of lithospheric mantle underlying TESZ.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The density of heat flow on the Earth’s surface (usually referred to as heat flow) is a function of many factors: heat inflow from the mantle, heat generation in the crust, heat conduction coefficient of rocks, initial temperature, etc. However, in many situations (e.g. old crust, no young magmatic activity, 1D geometry), a thermal steady state can be assumed. Then the surface heat flow is simply the sum of the heat flow at the lower boundary of the considered layer (which usually is the crust) and the total heat production in this layer. Heat production depends on the lithology of the layer, because the chemical composition of rocks determines the content of radioactive elements. The knowledge about surface heat flow and heat conduction in the crust enables to construct the geotherm (the function T(z), where z is the depth and T is the temperature), showing relationships between depth and temperature.
This simple relationship between heat flow and lithology does not occur in regions of young magmatism, where hot magma penetrating the lithosphere transfers additional heat that contributes to the observed surface heat flow. The influence of heat advection depends on the total heat delivered by the given volume of magma. In some regions, it may be irrelevant and short lived, but may be important in other areas, such as continental rifts.
The standard geophysical approach to heat flow and geotherms calculation is based on temperature measurements and large-scale simplistic models of the crust. The details of the geology are omitted (see, e.g. Furlong and Chapman 2013). In this paper, we couple the geological and geophysical data to assess the thermal state of individual crustal profiles. This non-standard detailed approach allows to compare the Moho heat flow in sites which are few tens of kilometres distant. Because the Moho heat flow cannot be directly measured, it is estimated by subtracting the crustal contribution from the surface heat flow. Therefore, potential error of Moho heat flow estimates may be significant.
The details of lithology, structure and evolution of subcontinental lithospheric mantle are well recognised in many areas thanks to numerous recent petrological studies (e.g. Puziewicz et al. 2015; Matusiak-Małek et al. 2017a, b, and references therein, in the part of Europe discussed in this paper). This knowledge, if coupled with relevant Moho heat flow models, would enable better understanding of current lithospheric mantle structure and dynamics.
We use the temperature measurements in the crust and hypothetical crustal profile to calculate the heat flow. Our example comes from copper mines situated in the Middle Odra Horst in the NE part of the Variscan orogen in SW Poland. To put these results in a broader context, we compare them with three other sites in the region, using the heat flow map of Majorowicz and Wybraniec (2011) as the starting point. One of the discussed sites enables the case model of disturbance of surface heat flow by Cenozoic volcanic activity. Our test sites are located across NE part of the Variscan orogen and SW part of TESZ in SW Poland (Fig. 1).
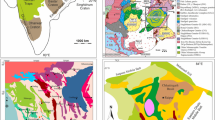
Location of lithological/thermal profiles (based on map of Franke 2014). The inset shows location of the study area relative to the major geological units of Central Europe (based on maps of Kroner et al. 2010; Franke et al. 2017). Surface heat flow after the map of Majorowicz and Wybraniec (2011) except Rudna, where surface heat flow after calculations of Majorowicz and Šafanda (2018). EEC East European Craton, TESZ Trans-European Suture Zone, BV Bruno-Vistulian microcontinent, VDF Variscan Deformation Front
Geological setting and rationale of site selection
The area considered in this study comprises NE part of the European Variscan orogen and SW part of Trans-European Suture Zone (Fig. 1). We discuss the sites in the Sudetic Block, in the Fore-Sudetic Monocline (Middle Odra and Wolsztyn–Leszno Horsts) and in the Szczecin–Miechów Synclinorium (Fig. 1). Except the Sudetes, Variscan rocks are buried beneath a few hundred-metre-thick cover of Tertiary and Quaternary sediments in the Middle Odra Horst, and under Permo-Mesozoic through Cenozoic cover in the Fore-Sudetic Monocline and Szczecin–Miechów Synclinorium. We follow the regional geological terminology proposed by Żelaźniewicz et al. (2011). Thus, we use the term Middle Odra Horst, proposed by Żelaźniewicz and Aleksandrowski (2008) instead of “Odra Fault Zone”, commonly used in older papers.
The NW–SE trending Middle Odra Horst (Oberc-Dziedzic et al. 1999; Dörr et al. 2006; Fig. 1) is ca. 200-km-long and up to 20-km-wide horst which separates the crystalline basement of the Bohemian Massif, exposed in the Sudetic and Fore-Sudetic Blocks (located to the SW) from the NE-ward-inclined crystalline concealed under thick cover of Permo-Triassic and Cenozoic sediments in the Fore-Sudetic Monocline. Two basement elevations (Bielawy–Trzebnica and Wolsztyn–Leszno Horsts) occur in the Fore-Sudetic Monocline. Boreholes revealed phyllites in their uppermost parts, overlain by Carboniferous flysch (Żelaźniewicz et al. 2003; Mazur et al. 2010a).
To the north of Wolsztyn–Leszno Horst, Permo-Mesozoic cover of the Szczecin–Miechów Synclinorium conceals several juxtaposed units within TESZ (Variscan Foreland sediments, Avalonian basement and accretionary prism, thinned Baltica lower crust) which nature and relationships are still the matter of debate (Żelaźniewicz et al. 2016; Mazur et al. 2015, and references therein). The underlying uppermost mantle is usually interpreted as prolongation of Baltica (e.g. Chyba et al. 2017; Kind et al. 2017), although Puziewicz et al. (2017) claimed that there is no continuation of Baltica mantle beneath Variscan Foreland. The Rheic suture (and corresponding contact between Saxothuringian and Rheno-Hercynian Zones) is supposedly located at the Middle Odra Horst (e.g. Franke 2014).
The geotherms presented in this study are based on hypothetical sections of the crust coupled with surface heat flow data from four sites: Wilcza Góra, Polkowice–Rudna, Święciechowa and Września (Fig. 1). We used the Wilcza Góra profile because of detailed petrological descriptions of lithospheric mantle xenoliths in the vicinity (Matusiak-Małek et al. 2014, 2017a, b) which enabled to define the model of basaltic melt migration through lithosphere and to model how the advective heat disturbs the steady-state heat flow. The Polkowice–Rudna profile was used because the temperature measurements from underground shafts of copper mines enabled the calculation of heat flow independent of older data. The Święciechowa and Września profiles were chosen for comparison with the two former ones because of drilling data, which enabled the precise lithological profiles of upper crust. All four profiles are arranged in line across the NE part of Variscan orogen in SW Poland and adjoining SW part of the Trans-European Suture Zone.
The Polkowice–Rudna and Września profiles are located close to major geological boundaries which are inclined. Therefore, the complete crustal profiles are not representative for the units cropping out at the surface. This is in fact the major problem in many studies of Variscan geology. Because both sites offer valuable data input to our models, we decided to use them.
Methods
Major lithological units of the investigated sites were characterised by 1D seismic models of the crust. To do this, we used recently published high-resolution 3D seismic P wave velocity model of the area of Poland, which describes lithospheric structure from the surface down to a depth of 60 km (Grad et al. 2016). Model of the uppermost several kilometres of sediments was built from over 100,000 geological boreholes, and vertical seismic profiling (VSP) from 1188 boreholes provided velocity data for regional tectonic units (Grad et al. 2016). This data set was supplemented by 2D velocity models from 32 deep seismic sounding refraction profiles which also provide information about the crust and uppermost mantle. The derived 3D velocity model contains six sedimentary layers (Tertiary and Quaternary, Cretaceous, Jurassic, Triassic, Permian and Pre-Permian) and three crustal layers (upper, middle and lower) and lithospheric mantle. Particularly, the model describes in detail the geometry of seismic basement (consolidated/crystalline crust) and Moho boundary (Grad and Polkowski 2016; Grad et al. 2016 and references therein). The seismic basement of the investigated area is characterised by velocities Vp < 6 km s−1, typical in most Phanerozoic structures of Western Europe. The Moho is at depth 29–33 km. The seismic velocities and thicknesses of the sedimentary layers, crystalline crust and uppermost mantle were extracted from 3D seismic model of the area of Poland (Fig. 2). We used the most probable rocks from each modelled region, and the data from drills if available (see “Lithological and thermal models along the studied cross section” for details).
To assess the heat budget in our profiles, we use heat flow map of Majorowicz and Wybraniec (2011), which is corrected for paleoclimatic effects. New heat flow data presented by Majorowicz and Šafanda (2018) and used in this paper are based on temperature gradients measured in the underground copper mine region in SW Poland and corrected surface temperature. The set of temperature measurements from underground copper mines in SW Poland was made available to us by KGHM Polska Miedź SA. They are made in progressing, unventilated shafts to plan the shaft ventilation. The details of measurement technique are given in Majorowicz and Šafanda (2018). The measurements of temperature Tz at depth z from Polkowice–Sieroszowice and Rudna mining areas and calculated thermal gradient are given in Table 1. Thermal conductivity for the upper sediments within the geothermal gradient (Grad T) of measured temperature T profile with depth z, T(z) (C/m), interval, was taken from nearby measured rocks by Majorowicz and Plewa (1979, 1984) to calculate heat flow Q (Table 1). We used three different values of the paleoclimatic correction (Majorowicz and Šafanda 2018) corresponding to three alternative models of the surface temperature means of the cold glacial phase and postglacial phase to calculate corrected T and heat flow (Table 1).
Heat production was calculated basing on physical parameters of rocks and their chemical composition taken from various sources, indicated in Tables 1, 3 and 4. The exception is the Polkowice–Rudna profile, which is based on rock densities, thermal conductivities and K, Th and U contents measured for this study (Table 3). The density of rocks was measured at the laboratory of the Institute of Oil and Gas in Cracow (Poland) by gas pycnometer AccuPyx II 1340 using helium. Thermal conductivities were measured at the laboratory of Institute of Geophysics, Czech Academy of Sciences, by optical scanning apparatus TCS (Lippmann and Rauen, Germany). Bulk-rock chemical analyses necessary to obtain K, Th and U contents were acquired in Bureau Veritas Mineral Laboratories in Vancouver, Canada, by ICP MS (procedure LF200, details available at http://www.bureauveritas.com).
Mantle heat flow and geotherms
Heat production (A in W/m3) of the rocks of the entire crust from surface to Moho (in the discussed area ca. 30 km) is calculated with the following approach. A is assigned to different crustal rock types characterised by different content of radiogenic elements of U, Th and K (Tables 1, 2, 3, 4). Heat production is computed from the measured and assumed based on rock type concentrations of U235, K40 and Th232 based on the relationship originally proposed by Birch (1954) and slightly modified later (Rybach 1988). Back-stripping of A generated heat contribution of these crustal rocks down to Moho depth yields Moho heat flow Qm. Surface heat flow Q0 will decrease with depth z as heat generation A(z):
where Q0 is heat flow at the surface.
Heat flow at Moho depth zmoho is
for z changing in 0 − zmoho interval.
The resulting values of heat flow and heat generation vs. depth z (Table 6) allow the construction of geotherms (Fig. 2), which are calculated based on heat flow, heat production and thermal conductivity models related to petrological models of the sedimentary rocks, crystalline crust and upper mantle from equations given by Hasterock and Chapman (2011) in their recent update of the method (their Eqs. 2 and 3).
Thermal conductivity of the crust and upper mantle at (z/T) conditions needs to be calculated for the geotherms to be calculated, because it is commonly measured in ambient conditions. Changes due to increase of temperature and pressure with depth z were calculated using Chapman and Furlong (1992) equation:
where λo is thermal conductivity at room temperature of 20 °C (293 K) and atmospheric pressure. The coefficient c represents pressure dependence in upper crust (c = 1.5 × 10−6 m−1), whereas the b coefficient was assumed to be b = 1.0 × 10−4 K−1 (Correia and Šafanda 2002). T is in kelvin. For mantle, we used a negative coefficient b = − 2.5 × 10−4 K−1 (Čermák et al. 1989). It reflects a gradually increasing radiative component of the heat transfer. The pressure dependence of conductivity within the mantle was neglected because it is not well constrained (2.5–4 Wm−1 K− 1) and the mantle geotherms in Fig. 2 and Table 6 are rather approximation.
Lithological and thermal models along the studied cross section
The Sudetic Block
The Sudetic Block and the Fore-Sudetic Block to the south of the central part of the Middle Odra Horst consist of low-grade metasedimentary and metavolcanic rocks forming the Kaczawa Fold Belt. The latter consists of low-grade metabasaltic rocks recording evolution from the continental to oceanic rifting (Furnes et al. 1994) and sedimentary sequences. Devonian–Lower Carboniferous melange successions which originated in the accretionary prism setting form the upper part of the Kaczawa Complex (Baranowski et al. 1990). In the close neighbourhood of the copper mining district, the Kaczawa rocks are pierced by Cenozoic alkaline volcanic rocks of the Złotoryja–Jawor Volcanic Complex (Puziewicz et al. 2015). The latter belongs to the set of Cenozoic volcanic complexes occurring to the NE of the northern termination of the Eger Rift along the Middle Odra Horst. The Jawor–Złotoryja complex is dominated by basanites with subordinate nephelinites, which erupted from 32 (Grodziec nephelinite; Badura et al. 2006) to 19 Ma (e.g. Krzeniów basanite; Birkenmajer et al. 2007); the 19–20 Ma lavas are most common.
The Wilcza Góra profile (Table 2) is located in the area of basanite outcrop at the outskirts of Złotoryja. In this site, the relatively thin sedimentary cover of Cretaceous and Permian–Upper Carboniferous sedimentary rocks of the North Sudetic Basin (Biernacka 2012 and references therein) is underlain by rocks of the Kaczawa Mts (the Złotoryja–Luboradz Unit, see Kryza et al. 2007 and references therein). The latter are Lower Palaeozoic mixed volcanic–sedimentary successions overlain by Devonian–Carboniferous melanges (Kostylew et al. 2017). The seismic profile (Fig. 2) shows an abrupt increase in P wave velocity at 22 km, which we interpret as the transition to the orthogneissic/granitic basement.
In our profile, we do not include basanites, which are thin (100–200 m) and discontinuous. We approximate the sedimentary rocks of the North Sudetic Basin by quartz arenites, although in reality the rocks occurring in neighbouring outcrop (Jerzmanice) contain few vol% of feldspar and are classified as subarkosic arenites (Biernacka 2012). The Kaczawa Mts. part of the profile is located at 1–22 km depth. It is represented by MORB-greenschist (ca. 40%), whereas the sedimentary and metasedimentary rocks are approximated by clay-rich mudstones (ca. 50%) with subordinate quartz-rich ones (ca. 10%) of the melange succession. Basing on seismic data, we speculate that the Kaczawa Mts. rocks are underlain by (3 km) layer of orthogneissic/granitic composition, which we approximate by the Izera granite. We do not use the more realistic Cadomian Wądroże Wielkie gneiss because of lack of high-quality analytical data, but this should not affect heat production assessment. The Wądroże Wielkie gneiss pierces the overlying low-grade metamorphic rocks of the Kaczawa fold belt. Its occurrence suggests that orthogneisses/granites may occur also in the upper part of the Kaczawa profile. The lower crust (from depth 25 km) is assumed to be similar to that modelled by Puziewicz et al. (2017) in Niedźwiedź (eastern part of the Fore-Sudetic Block), i.e. to consist of gabbros which are leucocratic in the upper part of the profile and whose content of clinopyroxene is increasing with depth. This model represents the quartzo-feldspathic lower crust injected with gabbros, which number and ratio of clinopyroxene to plagioclase increase towards the Moho.
The Middle Odra Horst
The Middle Odra Horst, beneath the Cenozoic sedimentary rocks, consists of medium-grade metamorphic rocks and granites (Oberc-Dziedzic et al. 1999; Dörr et al. 2006). The drillings piercing the sedimentary cover of the Middle Odra Horst showed occurrences of biotite–chlorite schists, locally with garnet (Polkowice), biotite (para) gneisses (Jędrzychów, Obora), phyllites and mica schists (Osiek; Kłapciński et al. 1975) intruded by unfoliated, I-type granodiorite to monzogranite intrusions (Oberc-Dziedzic et al. 1999), three of which are dated at 344–349 Ma (Dörr et al. 2006; Oberc-Dziedzic et al. 2015). Since these rocks were available to us thanks to the courtesy of prof. Teresa Oberc-Dziedzic, we analysed their chemical composition, measured density and heat conductivity and used in our model.
The Middle Odra Horst is possibly a continuation of the Mid-German Crystalline High. Therefore, the Odenwald and Spessart Mts. in Germany can serve as its exposed analogues. Odenwald Mts. are dominated by calc-alkaline igneous rocks of composition ranging from granite to gabbro, which form ca. 90% of the outcrop (Will et al. 2015; Altherr et al. 1999). Large part of the Spessart Mts. is considered to be the Avalonia rocks exposed in the tectonic window in overlying Gondwana-derived terranes (Will et al. 2017).
The Polkowice–Rudna profile (Table 3) is located in the copper mining district. The Polkowice drilling (159 m asl, Kłapciński et al. 1975) shows Quaternary sediments at 0–32 m, Tertiary at 32–403 m, Lower Buntsandstein at 403–577 m, Zechstein at 577–838 m, and Upper Rotliegendes at 838–1107 depth. Below Kłapciński et al. (1975) describe biotite schist with garnet. We approximate the sedimentary cover by 500 m of arkosic arenites, 300 m of limestones and 200 m of anhydrites. The thickness of sedimentary cover is approximated at 1000 m because the drillings (Osiek, Obora, Jędrzychów; Kłapciński et al. 1975) show that it is varying between ca 900 and 1100 m in Polkowice–Lubin area. We assume significant part of I-type granites (17 km in the 30-km-thick crust; represented by diorite from Nowiny and granodiorite from Przedmoście) with subordinate leucocratic gneiss (represented by sample from Kątna drilling, 1486 m depth) in the Polkowice–Rudna profile. The lower crust is considered to be amphibolitic. This is based on speculative assumption that it may be the relic amphibole-dominated cumulate rocks occurring in the lower parts of volcanic arc sections (e.g. Davidson et al. 2007 and references therein).
The Fore-Sudetic Monocline and Szczecin–Miechów Synclinorium
The Fore-Sudetic Monocline is a block in which poorly known basement is covered by Permo-Mesozoic succession of variable thickness and unconformably by approximately 350 m of Cenozoic sedimentary rocks (Mazur et al. 2010a). The Permo-Mesozoic rocks were deposited in several basins that developed in Permian across post-Variscan Europe (e.g. Polish Basin, Northeast German Basin). Their thickness increases from 1 km close to the Middle Odra Horst to around 5 km at the border between the Monocline and the Szczecin–Miechów Synclinorium (Mazur et al. 2010a). These sediments consist of siliciclastic and carbonate deposits and include also thick Zechstein evaporites (Grocholski 1975). The structure of the area was developed in Cretaceous during a compressional event that caused inversion of the Permo-Mesozoic basin fill and tilting of the Fore-Sudetic Monocline with the dip to the NE (Mazur et al. 2005).
Permian clastic Rotliegend sediments are intercalated with Upper Carboniferous to Permian volcanic rocks representing wide range of volcanic forms and compositions (Breitkreuz et al. 2007; Geißler et al. 2008; Żelaźniewicz et al. 2016). Currently, the volcanic rocks reside at a range of depths from approximately 2800 to over 6000 m (Maliszewska and Pokorski 1978; Breitkreuz et al. 2007; Żelaźniewicz et al. 2016). The volcanic field extending from the Northeast German Basin to the Polish Basin in the Szczecin–Miechów Synclinorium also varies in the thickness from several tens to over 2000 m (Benek et al. 1996; Paulick and Breitkreuz 2005; Geißler et al. 2008). Different areas are dominated by either silica-rich lava flows and lava domes (Mecklenburg-Vorpommern Sub-Province in north eastern Germany, Geißler et al. 2008) or ignimbrites and tuffs with rare lava flows (western Poland, Maliszewska and Pokorski 1978 and Flechtingen–Altmark Sub-Province in central Germany; Geißler et al. 2008) or predominantly andesitic shield volcanos (the Eastern Brandenburg Sub-Province and also extending into western Poland, Geißler et al. 2008). Generally, the thickness of the silica-rich volcanic rocks is larger in the German part of the basin with the rhyolitic rocks in northeastern Germany usually exceeding 500 m (Geißler et al. 2008), whereas rhyolitic tuff deposits located in the Fore-Sudetic Monocline have thickness below 500 m (Maliszewska and Pokorski 1978; Breitkreuz et al. 2007; Żelaźniewicz et al. 2016). The thickness of andesites varies from 0 to over 1400 m (drillcore Ośno IG2) and depends on the topography created by shield volcanos (Geißler et al. 2008). The silica-rich volcanic rocks are enriched in radiogenic elements compared to average upper continental crust (K2O = 2.8 wt%, Th = 10.5 ppm and U = 2.7 ppm, Rudnick and Gao 2003) as they contain 2.9–6.8 wt% of K2O, 12.1–25.9 ppm of Th and 2.3–5.3 ppm of U (Benek et al. 1996; Żelaźniewicz et al. 2016). In addition to volcanic rocks, over 250 m of granite (4096–4350 m, not drilled through) and 2-m granite xenolith surrounded by rhyolites at depth 3984–3986 m were recorded from the drillcore Chrzypsko-2 (Żelaźniewicz et al. 2016). Granite is older (302 Ma) than surrounding rhyolites (293 Ma, Żelaźniewicz et al. 2016), but has similar isotope and chemical composition (Żelaźniewicz et al. 2016; Słodczyk et al. 2018).
The Permo-Mesozoic sedimentary rocks overlay Carboniferous turbiditic succession of the thickness exceeding 2500 m, reduced in the areas of Bielawy–Trzebnica and Wolsztyn–Leszno Horsts, formed by Paleozoic phyllites metamorphosed at 340 Ma (Żelaźniewicz et al. 2003; Mazur et al. 2010a). Phyllites are the oldest lithology drilled in the basement of the Fore-Sudetic Monocline and are unconformably overlain by turbidites. Geochemistry and zircon chronology of the turbidites show that the sediments were derived from Devonian–Carboniferous continental volcanic arc (Mazur et al. 2010b).
The Święciechowa profile (Table 4) represents the Wolsztyn–Leszno Horst. We approximate the sedimentary cover of the Horst by sandstones underlain by limestones. The drilling and seismic data show that the low-grade crystalline basement starts at approximately 3 km depth with phyllites. By analogy with the parts of the Northern Phyllite Zone exposed in Germany (Oncken et al. 1995; Anderle et al. 1995), we assume that phyllites and greenschists are dominant mid-crustal lithologies. The lower crust is assumed—basing on the seismic data—to consist of thin diorite-dominated layer which rests on the garnet granulites.
The Września profile (Table 5) is representative for the SW part of the Trans-European Suture Zone. Its upper part is based on the drilling Września IG-1 (Mazur et al. 2010a; Maliszewska and Pokorski 1978), which was generalised to avoid multiple intercalations of rocks of identical heat production and conductivity. Carboniferous greywackes were the oldest drilled lithology and are extended down to 8 km based on the seismic profile (Fig. 2). The seismic data show increase in velocities at 8 km, which probably marks the surface of pre-Variscan basement represented by Lower Paleozoic sediments injected with Variscan or older intrusions. The presence of the Variscan granites in Carboniferous and pre-Carboniferous basement is consistent with the occurrence of upper part of a larger granite intrusion in the Chrzypsko drilling, also in the Szczecin–Miechów Synclinorium (Żelaźniewicz et al. 2016). Middle and lower crusts in Września are assumed to be similar to the Avalonian basement. This is based on the large-scale paleotectonic models of the European basement (e.g. Kroner et al. 2007; Franke 2014). The mid-crust is probably dominated by Cadomian gneisses, and the gneisses occurring within nearby Bruno-Vistulian microcontinent were used as analogues. The gneisses vary in composition and two sections with more and less evolved types were used in the profile construction. The lowermost crustal lithologies show seismic velocities typical for mafic basement and we linked it with the old Avalonian intermediate/mafic/ultramafic lower crust occurring in Burin Peninsula (Newfoundland, Murphy et al. 2008).
Discussion
The effect of advective heat transport on mantle heat budget
The geotherms presented in this study are constructed basing on the temperatures taken from the map of Majorowicz and Wybraniec (2011) or (Rudna site) calculated by Majorowicz and Šafanda (2018) on the basis of measurements in mine shafts and on speculative assumptions on rock types forming the crust and their compositions (namely K, U and Th contents). This standard steady-state approach results in the Moho heat flow and temperatures which are in fact defined by the crustal heat budget. The heat budget in lithospheric mantle is supposedly well represented by this approach, provided no heat is added to the mantle by percolating melts.
The part of SW Poland where the discussed sites are located was formed and stabilised during the Variscan Orogeny. The crystalline basement of European Variscan orogen was reactivated when the European Cenozoic Rift System (ECRIS) was formed in the foreland of growing Alps (Dèzes et al. 2004). Eger Rift in the western part of Bohemian Massif is the easternmost one of ECRIS rifts. Its formation was connected with the volcanism, which was active also in the area of Sudetic and Fore-Sudetic Blocks. The Cenozoic volcanism in Sudetes and Fore-Sudetic Block culminated at 34–26 and 22–18 Ma with very scarce eruptions between 5.5 and 1 Ma (K–Ar ages, Pécskay and Birkenmajer 2013 and references therein). It produced no continuous and thick lava sequences. The geochemical characteristics of Cenozoic lavas in this area show that the lavas come from asthenospheric sources, but local heating of the lithosphere was high enough to trigger its melting (Ladenberger et al. 2006).
Wilcza Góra is a basanite plug belonging to the Złotoryja–Jawor Volcanic Complex, the group of isolated Cenozoic lava occurrences (for details, see Puziewicz et al. 2015). The mantle xenolith suites from the Złotoryja–Jawor Volcanic Complex show that the nephelinitic lavas migrating through the lithospheric mantle at ca. 30 Ma heated it to ca. 1000–1100 °C (Matusiak-Małek et al. 2017a). The basanitic lavas of younger volcanic episode (ca. 20 Ma) bring to the surface xenoliths which show that the mantle peridotite temperatures were not re-equilibrated due to melt percolation and suggest that lithospheric mantle temperature was between ca. 830 and 890 °C (Matusiak-Małek et al. 2014). Therefore, the lithospheric mantle section beneath Wilcza Góra was affected by percolating “basaltic” melts, and we modelled the possible effects of advective heating on the local heat budget.
We assume that lithospheric mantle section beneath the Złotoryja–Jawor Volcanic Complex was affected by lavas migrating from the asthenosphere between 30 and 18 Ma, which had the temperature of 1400 °C (asthenospheric basanite solidus). The affected mantle area is 20 × 40 km (crude approximation of the Złotoryja–Jawor Volcanic Complex lateral size) and was located at depth from 55 to 40 km (i.e. spinel peridotite facies). The case studies of mantle xenolith suites from the area (Puziewicz et al. 2011; Matusiak-Małek et al. 2010, 2014, 2017a, b; Kukuła et al. 2015) show that the lava flow through the mantle was channelized in fissures of centimetric to decimetric thickness, and the melt percolated pervasively in the neighbouring mantle peridotite. To model this situation, we assume that the discussed hypothetical mantle was instantly injected with melt. After injection, the mantle consisted of 80 vol% of solid peridotite and 20 vol% of melt, and subsequently cooled. The injections happened at 29.9, 28 and 18 Ma, the size of melt-percolated region was 20 × 40 km and it was located at depth from 40 to 55 km. The heat flow and temperature modelling (Fig. 3) show that the present disturbance in surface heat flow is slight (ca. 4 mW/m2), as well as that of Moho heat flow (3 mW/m2). The graphs showing spatial variation in temperature vs. time plus more detailed description of modelling are shown in Appendix. The surface heat flow effect is close to the uncertainties in the heat flow estimates, which in our opinion are within a few mW/m2, and are due to various log temperature measurement errors. Therefore, our model shows that the volcanic events which occurred in the Cenozoic in Lower Silesia affected very slightly the current heat flow both on the surface and on Moho.
The effect of magma percolation in the lithospheric mantle during Cenozoic volcanism in the model volcanic system in SW Poland (see text for details). The model is representative of the Wilcza Góra profile. a Temperature profiles in the centre of modelled domain: before volcanism (steady-state geotherm), at 16 Ma (2 Ma after third magma pulse), and at 1 Ma (before glaciation); b relationships between time and heat flow at various depths
The older models accounting for Cenozoic melt percolation in lithosphere were presented (Čermák et al. 1996; Christensen et al. 2001). Čermák et al. (1996) modelled a large magma chamber (14 km across and 5 km thick) located immediately above Moho which cools from 1300 °C, assuming also occurrence of shallow reservoirs of lava supplying massive surface activity. They assumed that magmatism started 80 Ma. Their model was used to approximate the extensive volcanic activity in the SW part of the Eger Rift. It shows that even this extreme situation has little effect on the recent surface heat flow (< 3 mW/m2). Similar model was presented also by Christensen et al. (2001) who modelled layer of basaltic magma at similar conditions (5 km thickness, 1300 °C) and location (immediately above Moho) at 35–30 Ma and cooling after this time. These authors assumed no effect of underplating on current geotherm and heat flow.
The effect of assumed crustal lithologies on mantle heat flow
The values of mantle heat flow calculated by us (Table 6) are sensitive to both surface heat flow measurements and assumed lithology of the crust. We believe that palaeoclimate-corrected surface heat flow we use (after map of Majorowicz and Wybraniec 2011) is the best approximation. This map is reliable especially in the area to the NE Middle Odra Horst, where the granitoids which could disturb the general pattern of heat production, if any, occur under thick sedimentary cover. In the Middle Odra Horst and to SE of it, the granitoids occurring close to the surface possibly generate local kilometre-scale variation in the surface heat flow, similar to those described in Erzgebirge by Förster and Förster (2000). This kind of strongly increased heat flow occurs in the Polkowice–Rudna profile and is discussed in detail below.
The lithologies we propose are based on assessment of local geological structure and rocks which really or supposedly form it. However, the deeper parts of our profiles are only estimates of real rock sequences in each profile. These estimates are based on (1) seismic profiles of each site to which (2) the geologically reasonable rock sequences were fitted (Fig. 2).
The surface heat flow in Wilcza Góra is assumed to be 66 mW/m2, whereas the calculated Moho heat flow is 34 mW/m2, which is relatively of high value compared to second estimate in the Sudetic and Fore-Sudetic Blocks (28 mW/m2 in Niedźwiedź, Puziewicz et al. 2012). The Moho heat flow values between 20 and 30 mW/m2 are estimated to be located ca. 200 km to the west Erzgebirge by Förster and Förster (2000). The higher than regional Moho heat flow can be explained as (1) the artefact caused by significant participation of greenschist and resulting low heat production in the profile or (2) real observation.
The heat flow of 84 mW/m2 in Polkowice–Rudna is surface extrapolation of heat flow measured in underground shafts of copper mines. It is high because of elevated heat production in the granitoids of the Middle Odra Horst (Table 3). The crystalline basement of the Middle Odra Horst occurs at depths of ca. 300–1100 in its part located between Szprotawa and Wrocław (drilling data in Kłapciński et al. 1975) and is rich in granites (Oberc-Dziedzic et al. 1999). Therefore, we are of the opinion that the locally high (> 80 mW/m2) surface heat flow is the manifestation of abundant granite occurrences in the Middle Odra Horst. Since the heat production is concentrated in the upper crust, the Moho heat flow 28 mW/m2 is similar to the other estimates in the region.
In this paper, we use lithological models of the crust for the heat generation/heat-flow with depth and geotherm calculation. The different approach to geotherm construction was presented by Majorowicz and Šafanda (2018), who used only seismic data and geophysical models to calculate heat generation/heat flow with depth and geotherms for the Polkowice–Rudna area using the same set of temperature measurements for the range of paleoclimatic models 1–3 discussed in detail in their paper. The variation of heat flow estimate (82–87 mW/m2) is due to uncertainty of the paleoclimatic models. In this study, we are using the low end of the calculated heat flow range, based on the paleoclimatic model 1 of Majorowicz and Šafanda (2018). We assume it to be the most realistic one as being closest to previous heat flow map (Majorowicz and Wybraniec 2011) based on well temperature logs, and we use it for farther calculations (mantle heat flow and geotherms). The Moho heat flow calculated by Majorowicz and Šafanda (2018) for all three paleoclimatic models varies between 37 and 41 mW/m2, and is higher than the estimate presented in this study and beyond the values typical for eastern part of Saxothuringicum, which supposedly are close to 28–30 mW/m2 (see “Regional geological considerations”). These differences are, however, relatively small considering the uncertainty of Moho heat flow determination, which is usually > 10% and as high as 20% (i.e. ca. 3–6 mW/m2). Nevertheless, these two results show how important is the assessment of local crustal lithology in estimation of mantle heat flow.
Potential errors and perspective
The approach presented by us is based on geological cross sections of lithosphere in a certain points, surface heat flow measurements and laboratory measurements of rock parameters (contents of heat producing elements, conductivity and density). All of them are subjected to errors.
The cross sections rely on geological models paired with seismic data. They are always more or less speculative below the maximal drilling depth, which usually does not exceed 8–10 km. The heat flow measurements are made in drilling wells, and are subjected to errors which typically are within the range of 1–5 mW/m2 (Jaupart and Mareschal 2015, their Table 4). These point measurements are extrapolated when heat flow map is prepared. These uncertainties are difficult to assess quantitatively because their major source is the lithological interpretation (see also the discussion in “The effect of assumed crustal lithologies on mantle heat flow”).
The intention of our study was, among others, to show that the progress in knowledge on the crust of Variscan orogen of Europe makes now possible to define basic “styles” of the crust. The data on heat-producing elements, if paired with rocks, enable the calculation of heat budget in each crust type (in fact this is the extension of classical idea of “heat flow provinces”). With this kind of models the regional scale the crustal geothermal variation could be defined, and that would make the step towards the more realistic Moho temperatures estimates in the regional scale.
The laboratory measurements of rock density measurements as well as the chemical analyses are highly precise now and their contribution to the overall uncertainty of the calculated heat budget is minor. To demonstrate this, we calculated the differences in surface heat flow, which would arise from a layer of rock located between the surface and 10 km depth, using lower and upper limits of their density measurements and heat producing element analyses (for measurement and analytical details see “Methods”). We used the gneiss from Kątna drilling a granite from Przyborowice drilling. Their densities are measured with ± 0.013 g/cm3 error. The error in K2O determination is ± 0.1 wt%, U ± 0.1 ppm and Th 0.2 ppm. We assumed the heat flow at the base of discussed layer to be 50 mW/m2. The results of our 1D stationary simulation show that the differences due to density measurements and chemical analytical errors are 1.43 (gneiss) and 0.56 (granite) mW/m2 (Table 7) and that the decision on rock type in the profile is more important than analytical errors.
Regional geological considerations
The surface measurements of heat flow as well as Moho heat flow calculations are both subjected to significant errors (e.g. Jaupart and Mareschal 2015). Mareschal and Jaupart (2004) indicate that the large-scale, geological structure-independent (> 500 km) variation of Moho heat flow is less than ± 2 mW/m2 and thus smaller than “detection limit” of heat flow studies. Our example shows that small-scale Moho heat flow estimates can vary significantly. Despite significant potential errors (see the example of Polkowice–Rudna described above), the data on Moho heat flow can supply information on lithospheric mantle dynamics complementary to other kinds of information on mantle.
The Moho heat flow seems to be close to 30 mW/m2 in the Saxothuringian part of the Bohemian Massif. Förster and Förster (2000) calculated the values between 20 and 30 mW/m2 in Erzgebirge. Puziewicz et al. (2012) indicate 28 mW/m2 in the eastern part of Fore-Sudetic Block. The models presented in this study suggest similar values of Moho heat flow: 34 mW/m2 in Wilcza Góra (central part of Sudetes) and 28 mW/m2 in Polkowice–Rudna (Middle Odra Horst). The Moho heat flow in Święciechowa (27 mW/m2) fits these values, albeit the site is located in the Wolsztyn–Leszno Horst, thus within the eastern counterpart of the Rheno-Hercynian Zone.
The lithospheric mantle underlying Saxothuringian part of the Bohemian Massif shows consistent seismic anisotropy (e.g. Plomerová et al. 2012) and supposedly represents the continuous fragment of a lithospheric plate docked to the orogen in Variscan times. The presented data indicate that the Moho heat flow close to 28–30 mW/m2 is a characteristic steady-state value for this region.
Förster and Förster (2000) suggested that relatively high Moho heat flow in Erzgebirge may be due to advective heating by Cenozoic volcanism, which was active in the region, or due to chemical characteristics of the mantle peridotites themselves. Our data for the Saxothuringian part of the Bohemian Massif show that volcanic activity enlarges the Moho heat flow outside the Eger Rift only locally and slightly. Thus, the relatively high Moho heat flow value results rather from the lithological characteristics of mantle lithosphere. The Moho heat flow in the Eger Rift itself is probably higher due to significant transient volcanic component.
The Moho heat flow is significantly higher (36 mW/m2) in Września, which is located in the TESZ. High surface (up to 90 mW/m2; Majorowicz 2004; Majorowicz et al. 2003) and Moho (> 35 mW/m2; Majorowicz 2004) heat flow are a regional feature characteristic for SW part of TESZ. This enlarged heat flow area occurs between the Middle Odra Horst to SW and the Variscan Deformation Front to NE (cf. Figures 13 and 14 in Szewczyk and Gientka 2009, Fig. 2 in; Majorowicz 1978, Fig. 1 in; Majorowicz and Wybraniec 2011 and Fig. 2 in; Majorowicz and Šafanda 2018) despite the differences in absolute heat flow values due to differences in thermal conductivity models, estimated from well logs (Szewczyk and Gientka 2009) versus measured on cores (Majorowicz and Wybraniec 2011). It continues to NE part of the German Basin, where average surface heat flow 77 ± 3 mW/m2 reaches up to 91 mW/m2 for the 68–91 range (Norden et al. 2008). This Moho heat flow, which indicates “warm” lithospheric mantle, can be an artefact, resulting from underestimation of volume of rhyolites/granites related to the Permian igneous province. The variable thickness and composition of volcanic rocks drilled over the Permian basins in Germany and Poland show that it is not straightforward to estimate the real volume of igneous rocks and their contribution to heat budget (see “Lithological and thermal models along the studied cross section”). On the other hand, the available seismic data and geological models indicate that mantle lithosphere underlying the Rheno-Hercynian Zone represents separate lithospheric plate and differs by seismic anisotropy from its surroundings (Babuška and Plomerová 2006) and also the sub-lithospheric upper mantle exhibits seismic features different from those of Saxothuringicum (Kind et al. 2017). This could result in differences in thermal properties and enlarged Moho heat flow.
Conclusions
Surface heat flow measurements are subjected to significant errors (1–5 mW/m2, Jaupart and Mareschal 2015, their Table 4). Nevertheless, they bring important information on the geological structure of lithosphere. We coupled the surface heat flow information with the calculations of lithospheric heat production in four sites in SW Poland, which enabled discussion about the Moho heat flow.
Our calculations show that Moho heat flow beneath Sudetic and Fore-Sudetic Blocks is close to 30 mW/m2. It is similar to upper limit of mantle heat flow beneath Erzgebirge (Förster and Förster 2000). We are of the opinion that this value of Moho heat flow is representative of the Saxothuringian part of the Bohemian Massif (Sudetes and Erzgebirge) and it reflects the thermal characteristics of underlying lithospheric and sub-lithospheric mantle.
Higher value of Moho heat flow (36 mW/m2) is shown by reconnaissance calculation in a site located in the SW part of Trans-European Suture Zone. It fits the earlier estimates of Majorowicz (2004 and references therein). We suggest that this is due to different thermal characteristics of lithospheric mantle underlying the TESZ in Poland.
The Variscan orogen of Europe was subjected to rifting and volcanism during Cenozoic, and the lithospheric mantle was infiltrated by the lavas moving to the surface. In Poland, the volcanism was concentrated in the Sudetic- and Fore-Sudetic Blocks. The new petrological data (Matusiak-Małek 2017a and references therein) enabled the precise model of thermal effect of volcanism on the lithospheric mantle. It shows that syn-volcanic melt residence in the lithospheric mantle leads to small (< 4 mW/m2) increase of the current Moho and surface heat flow.
References
Altherr R, Henes-Klaiber U, Hegner E, Satir M, Langer C (1999) Plutonism in the Variscan Odenwald (Germany): from subduction to collision. Int J Earth Sci 88:422–443
Anderle H-J, Franke W, Schwab M (1995) Rhenohercynian foldbelt, metamorphic units (Northern Phyllite Zone, stratigraphy). In: Dallmayer RD, Franke W, Weber K (eds) Pre-Permian geology of Central and Eastern Europe. Springer, Berlin, pp 99–107
Babuška V, Plomerová J (2006) European mantle lithosphere assembled from rigid microplates with inherited seismic anisotropy. Phys Earth Planet Inter 158:264–280
Badura J, Pécskay Z, Koszowska E, Wolska A, Zuchiewicz W, Przybylski B (2006) New data on age and petrological properties of Lower Silesian basaltoids, SW Poland. Przegląd Geologiczny 54:145–153 (in Polish, English abstr.)
Baranowski Z, Haydukiewicz A, Kryza R, Lorenc S, Muszyński A, Solecki A, Urbanek Z (1990) Outline of the geology of the Góry Kaczawskie (Sudetes, Poland). Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie Abhandlungen 179:223–257
Benek R, Kramer W, McCann T, Scheck M, Negendank JFW, Korich D, Huebscher HD, Bayer U (1996) Permo-carboniferous magmatism of the Northeast German Basin. Tectonophysics 266:379–404
Biernacka J (2012) Provenance of Upper Cretaceous quartz-rich sandstones from the North Sudetic Synclinorium, SW Poland: constraints from detrital tourmaline. Geol Q 56:315–332
Biernacka J, Borysiuk K, Raczyński P (2005) Zechstein (Ca1) limestone-marl alternations from the North-Sudetic Basin, Poland: depositional or diagenetic rhythms? Geol Q 49:1–14
Birch F (1954) Heat from radioactivity. In: Faul H (ed) Nuclear geology. Wiley, New York, pp 148–174
Birkenmajer K, Pécskay Z, Grabowski J, Lorenc MW, Zagożdżon PP (2007) Radiometric dating of the Tertiary volcanics in Lower Silesia, Poland. V. K-Ar and palaeomagnetic data from Late Oligocene to Early Miocene basaltic rocks of the North-Sudetic Depression. Ann Soc Geol Pol 77:1–16
Breitkreuz C, Kennedy A, Geißler M, Ehling B, Kopp J, Muszyński A, Protas A (2007) Far Eastern Avalonia: its chronostratigraphic structure revealed by SHRIMP zircon ages from Upper Carboniferous to Lower Permian volcanic rocks (drill cores from Germany, Poland, and Denmark). Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 423:173–189
Čermák V, Šafanda J, Guterch A (1989) Deep temperature distribution along three profiles crossing the Teisseyre–Tornquist tectonic zone in Poland. Tectonophysics 164:151–163
Čermák V, Šafanda J, Krešl M, Kučerová L (1996) Heat flow studies in Central Europe with special emphasis on data from former Czechoslovakia. Glob Tecton Metallog 5:109–123
Chapman DS, Furlong KP (1992) The thermal state of the lower crust. In: Fountain DM, Arculus RJ, Kay RM (eds) Developments in geotectonics. Continental lower crust, vol 23. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 179–199
Christensen NI, Medaris LG Jr, Wang HF (2001) Depth variation of seismic anisotropy and petrology in central European lithosphere: a tectonothermal synthesis from spinel lherzolite. J Geophys Res 106B1:645–664
Christensen NI, Mooney WD (1995) Seismic velocity structure and composition of the continental crust: a global view. J Geophys Res 100B7:9671–9788
Chyba J, Plomerová J, Vecsey L, Munzarová H (2017) Tomography study of the upper mantle around TESZ based on PASSEQ experiment data. Phys Earth Planet Inter 266:29–38
Correia A, Šafanda J (2002) Geothermal modelling along a two-dimensional crustal profile in Southern Portugal. J Geodyn 34:47–61
Czechowski L (1993) Theoretical approach to mantle convection. In: Teisseyre R, Czechowski L, Leliwa-Kopystyński J (eds) Dynamics of the Earth’s evolution. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 161–271
Davidson J, Turner S, Handley H, Macpherson C, Dosseto A (2007) Amphibole “sponge” in arc crust? Geology 35:787–790
Dèzes P, Schmid SM, Ziegler PA (2004) Evolution of the European Cenozoic Rift Systems: interaction of the Alpine and Pyrenean orogens with their foreland lithosphere. Tectonophysics 389:1–33
Dörr W, Żelaźniewicz A, Bylina P, Schastok J, Franke W, Haack U, Kulicki C (2006) Tournaisian age of granitoids from the Odra Fault Zone (southwestern Poland): equivalent of the Mid-German Crystalline High? Int J Earth Sci 95:341–349
Förster A, Förster H-J (2000) Crustal composition and mantle heat flow: implications from surface heat flow and radiogenic heat production in the Variscan Erzgebirge (Germany). J Geophys Res 105B12:27917–27938
Franke W (2014) Topography of the Variscan orogen in Europe: failed-not collapsed. Int J Earth Sci 103:1471–1499
Franke W, Cocks LRM, Torsvik TH (2017) The Palaeozoic oceans revisited. Gondwana Res 48:257–284
Furlong KP, Chapman DS (2013) Heat flow, heat generation and the thermal state of the lithosphere. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 41:385–410
Furnes H, Kryza R, Muszyński A, Pin C, Garmann LB (1994) Geochemical evidence for progressive, rift-related early Palaeozoic volcanism in the western Sudetes. J Geol Soc Lond 151:91–109
Geißler M, Breitkreuz C, Kiersnowski H (2008) Late Paleozoic volcanism in the central part of the Southern Permian Basin (NE Germany, W Poland): facies distribution and volcano-topographic hiati. Int J Earth Sci 97:973
Grad M, Polkowski M (2016) Seismic basement in Poland. Int J Earth Sci 105:1199–1214
Grad M, Polkowski M, Ostaficzuk SR (2016) High-resolution 3D seismic model of the crustal and uppermost mantle structure in Poland. Tectonophysics 666:188–210
Grocholski W (1975) Variscides of southern Wielkopolska. Przegląd Geologiczny 23(4):171–174 (In Polish)
Hasterock D, Chapman DS (2011) Heat production and geotherms for the continental lithosphere. Earth Planet Sci Lett 307:59–70
Jaupart C, Mareschal J-C (2015) Heat flow and thermal structure of the lithosphere. In: Schubert G (editor-in-chief) Treatise on geophysics, 2nd edn, vol 6. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 217–253
Kind R, Handy MR, Yuouan Z, Meier T, Kämpf H, Soomro R (2017) Detection of a new sub-lithospheric discontinuity in Central Europe with S-receiver functions. Tectonophysics 700–701:19–31
Kłapciński J, Juroszek Cz, Sachanbiński M (1975) New data on geology of the Fore-Sudetic crystalline basement. Geol Sudet 10(2):7–46 (in Polish, English summary)
Kostylew J, Zalasiewicz JA, Kryza R (2017) Pervasive near-surface stratal disruption in an accretionary prism setting: Kaczawa Complex, SW Poland. Geol Mag 154:651–660
Kowal-Linka M, Jochum K (2015) Variability of trace element uptake in marine reptile bones from three Triassic sites (S Poland): influence of diagenetic processes on the host rock and significance of the applied methodology. Chem Geol 397:1–13
Kroner U, Hahn T, Romer RL, Linnemann U (2007) The Variscan orogeny in the Saxo-Thuringian Zone—heterogeneous overprint of Cadomian/Paleozoic Peri-Gondwana crust. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 423:153–172
Kroner U, Romer RL, Linnemann U (2010) The Saxo-Thuringian Zone of the Variscan orogen as part of Pangea. In: Linnemann U, Romer RL (eds) From the Cadomian Active Margin to the Variscan Orogen: the pre-Mesozoic Geology of Saxo-Thuringia (NE Bohemian Massif). E. Schweizerbart Science Publishers, Stuttgart, pp 3–16 In
Kryza R, Zalasiewicz J, Mazur S, Aleksandrowski P, Sergeev S, Larionov A (2007) Precambrian crustal contribution to the Variscan accretionary prism of the Kaczawa Mountains (Sudetes, SW Poland): evidence from SHRIMP dating of detrital zircons. Int J Earth Sci 96:1153–1162
Kukuła A, Puziewicz J, Matusiak-Małek M, Ntaflos T, Büchner J, Tietz O (2015) Depleted subcontinental lithospheric mantle and its tholeiitic melt metasomatism beneath NE termination of the Eger Rift (Europe): the case study of the Steinberg (Upper Lusatia, SE Germany) xenoliths. Mineral Petrol 109:761–787
Ladenberger A, Michalik M, Tomek C, Peate DW (2006) Alkaline magmatism in SW Poland: an example of asthenosphere-lithosphere interactions? Mineral Pol Spec Pap 29:40–47
Losiak A, Czechowski L, Velbel MA (2015) Ephemeral liquid water at the surface of the Martian North Polar Residual Cap: results of numerical modeling. Icarus 262:131–139
Majorowicz J (1978) Mantle heat flow and geotherms for major tectonic units in Central Europe. Pure Appl Geophys 117:109–123
Majorowicz J (2004) Thermal lithosphere across the Trans-European Suture Zone in Poland. Geol Q 48:1–14
Majorowicz J, Plewa S (1979) Study of heat flow in Poland with special regard to tectonophysical problems. In: Čermak V, Rybach L (eds) Terrestrial heat flow in Europe. Springer, Berlin, pp 240–252
Majorowicz J, Šafanda J (2018) Lithosphere thickness from new heat-flow data of the Odra Variscan Area, SW Poland. Pure Appl Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-1941-7
Majorowicz J, Wybraniec S (2011) New terrestrial heat flow map of Europe after regional paleoclimatic correction application. Int J Earth Sci 100:881–887
Majorowicz JA, Čermak V, Šafanda J, Krzywiec P, Wróblewska M, Guterch A, Grad M (2003) Heat flow models across the Trans-European Suture Zone in the area of the POLONAISE’97seismic experiment. Phys Chem Earth 28:375–391
Maliszewska A, Pokorski J (1978) Pyroclastic rocks of the Obrzycko Member (Autunian) in the western part of the Polish Lowlands. Kwartalnik Geologiczny 22(3):511–532
Mareschal JC, Jaupart C (2004) Variations of surface heat flow and lithospheric thermal structure beneath the North American craton. Earth Planet Sci Lett 223:65–77
Matusiak-Małek M, Puziewicz J, Ntaflos T, Grégoire M, Downes H (2010) Metasomatic effects in the lithospheric mantle beneath the NE Bohemian Massif: a case study of Lutynia (SW Poland) peridotitic xenoliths. Lithos 117:49–60
Matusiak-Małek M, Puziewicz J, Ntaflos T, Grégoire M, Benoit M, Klügel A (2014) Two contrasting lithologies in off-rift subcontinental lithospheric mantle beneath Central Europe—the Krzeniów (SW Poland) case study. J Petrol 55:1799–1828
Matusiak-Małek M, Ćwiek M, Puziewicz J, Ntaflos T (2017a) Thermal and metasomatic rejuvenation and dunitization in lithospheric mantle beneath Central Europe—the Grodziec (SW Poland) case study. Lithos 276:15–29
Matusiak-Małek, Puziewicz J, Ntaflos T, Grégoire M, Kukuła A, Wojtulek P (2017b) Origin and evolution of rare amphibole-bearing mantle peridotites from Wilcza Góra (SW Poland), Central Europe: xenolith suite case. Lithos 286–287:302–323
Mazur S, Scheck-Wenderoth M, Krzywiec P (2005) Different modes of the Late Cretaceous–Early Tertiary inversion in the North German and Polish basins. Int J Earth Sci 94:782–798
Mazur S, Aleksandrowski P, Turniak K, Krzemiński L, Mastalerz K, Górecka-Nowak A, Kurowski L, Krzywiec P, Żelaźniewicz A, Fanning MC (2010a) Uplift and late orogenic deformation of the Central European Variscan belt as revealed by sediment provenance and structural record in the Carboniferous foreland basin of western Poland. Int J Earth Sci 99:47–64
Mazur S, Kroner A, Szczepański J, Turniak K, Hanzl P, Melichar R, Rodionov NV, Paderin I, Sergeev SA (2010b) Single zircon U–Pb ages and geochemistry of granitoid gneisses from SW Poland: evidence for an Avalonian affinity of the Brunian microcontinent. Geol Mag 147:508–526
Mazur S, Mikołajczak M, Krzywiec P, Malinowski M, Buffenmyer V, Lewandowski M (2015) Is the Teisseyre–Tornquist Zone an ancient plate boundary of Baltica? Tectonics 34:2465–2477
Murphy JB, McCausland PJA, O’Brien SJ, Pisarevsky S, Hamilton MA (2008) Age, geochemistry and Sm–Nd isotopic signature of the 0.76 Ga Burin Group: compositional equivalent of Avalonian basement? Precambrian Res 165:37–48
Norden B, Förster A, Ballig N (2008) Heat flow and lithospheric thermal regime in the Northeast German Basin. Tectonophysics 460:215–229
Oberc-Dziedzic T, Żelaźniewicz A, Cwojdziński S (1999) Granitoids of the Odra Fault Zone: late- to post-orogenic Variscan intrusions in the Saxothuringian Zone, SW Poland. Geol Sudet 32:55–71
Oberc-Dziedzic T, Pin C, Kryza R (2005) Early Palaeozoic crustal melting in an extensional setting: petrological and Sm–Nd evidence from the Izera granite-gneisses, Polish Sudetes. Int J Earth Sci 94:354–368
Oberc-Dziedzic T, Kryza R, Pin C (2015) Variscan granitoids related to shear zones and faults: examples from the Central Sudetes (Bohemian Massif) and the Middle Odra Fault Zone. Int J Earth Sci 104:1139–1166
Oncken O, Franzke HJ, Dittmar U, Klügel Th (1995) Rhenohercynian foldbelt, metamorphic units (Northern Phyllite Zone, structure). In: Dalmayer RD, Franke W, Weber K (eds) Pre-Permian geology of Central and Eastern Europe. Springer, Berlin, pp 108–117
Paulick H, Breitkreuz C (2005) The Late Paleozoic felsic lava-dominated large igneous province in northeast Germany: volcanic facies analysis based on drill cores. Int J Earth Sci 94:834–850
Pécskay Z, Birkenmajer K (2013) Insight into the geochronology of Cenozoic alkaline basaltic volcanic activity in Lower Silesia (SW Poland) and adjacent areas. In: Büchner J, Rapprich V, Tietz O (eds) Basalt 2013—Cenozoic magmatism in Central Europe, abstract & excursion guides, Czech Geological Survey, Prague and Senckenberg Museum of Natural History Görlitz, pp 66–67
Plewa S (1984) Distribution of geothermal parameters on the territory of Poland. Publications of the Center for Basic Problems of Mineral Raw Materials and Energy Management, Polish Academy of Sciences, Krakow, pp 1–38
Plomerová J, Vecsey L, Babuška V (2012) Mapping seismic anisotropy of the lithospheric mantle beneath the northern and eastern Bohemian Massif (central Europe). Tectonophysics 564–565:38–53
Puziewicz J, Koepke J, Grégoire M, Ntaflos T, Matusiak-Małek M (2011) Lithospheric mantle modification during Cenozoic rifting in Central Europe: evidence from the Księginki nephelinite (SW Poland) xenolith suite. J Petrol 52:2107–2145
Puziewicz J, Czechowski L, Krysiński L, Majorowicz J, Matusiak-Małek M, Wróblewska M (2012) Lithosphere thermal structure at the eastern margin of the Bohemian Massif: a case petrological and geophysical study of the Niedźwiedź amphibolite massif (SW Poland). Int J Earth Sci 101:1211–1228
Puziewicz J, Matusiak-Małek M, Ntaflos T, Grégoire M, Kukuła A (2015) Subcontinental lithospheric mantle beneath Central Europe. Int J Earth Sci 104:1913–1924
Puziewicz J, Polkowski M, Grad M (2017) Geophysical and petrological modeling of the lower crust and uppermost mantle in the Variscan and Proterozoic surroundings of the Trans-European Suture Zone in Central Europe. Lithos 276:3–14
Rudnick RL, Gao S (2003) Composition of the continental crust. In: Rudnick RL (ed) The crust, vol. 3. Elsevier, New York, pp 1–64
Rybach L (1988) Determination of heat production rate. In: Haenel R, Rybach L, Stegena L (Eds) Handbook of terrestrial heat-flow density determination. Kluwer Academic Press, Norwell, pp 125–142
Słodczyk E, Pietranik A, Glynn S, Wiedenbeck M, Breitkreuz C, Dhuime B (2018) Contrasting sources of Late Paleozoic rhyolite magma in the Polish Lowlands: evidence from U-Pb zircon ages, Hf and O isotope composition. Int J Earth Sci 107:2065–2081
Szewczyk J, Gientka M (2009) Terrestrial heat flow density in Poland—a new approach. Geol Q 53:125–140
Turcotte DL, Schubert G (2001) Geodynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 456
Will TM, Lee S-H, Schmädicke E, Frimmel HE, Okrusch M (2015) Variscan terrane boundaries in the Odenwald–Spessart basement, Mid-German Crystalline Zone: new evidence from ocean ridge, intraplate and arc-derived metabasaltic rocks. Lithos 220–223:23–42
Will TM, Schulz B, Schmädicke E (2017) The timing of metamorphism in the Odenwald–Spessart basement, Mid-German Crystalline Zone. Int J Earth Sci 106:1631–1649
Żelaźniewicz A, Aleksandrowski P (2008) Tectonic subdivision of Poland: southwestern Poland. Przegląd Geologiczny 56:904–911 (in Polish, English abstr)
Żelaźniewicz A, Marheine D, Oberc-Dziedzic T (2003) A Late Tournaisian synmetamorphic folding and thrusting event in the eastern Variscan foreland: 40Ar/39Ar evidence from the phyllites of the Wolsztyn–Leszno High, Western Poland. Int J Earth Sci 92:185–194
Żelaźniewicz A, Aleksandrowski P, Buła Z, Karnkowski PH, Konon A, Oszczypko N, Ślączka A, Żaba J, Żytko K (2011) Tectonic regionalization of Poland. Committee of Geological Sciences of Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw, pp 1–60 (in Polish only)
Żelaźniewicz A, Oberc-Dziedzic T, Fanning CM, Protas A, Muszyński A (2016) Late Carboniferous–early Permian events in the Trans-European Suture Zone: tectonic and acid magmatic evidence from Poland. Tectonophysics 675:227–243
Acknowledgements
We express our thanks to KGHM Polska Miedź SA for making available for us the temperature measurements in mine shafts. We are grateful to Prof. Teresa Oberc-Dziedzic (University of Wrocław) for access to her drilling core collection from Fore-Sudetic Monocline, which enabled us to measure the physical and chemical data presented in Table 3. We thank Dr. Joanna Kostylew (University of Wrocław) for providing her unpublished data on chemical composition of metasedimentary rocks of the Kaczawa Mts. We thank the Reviewers (Andrzej Żelaźniewicz, Wolfram Geissler and Anonymous) for thoughtful comments on the earlier version of the paper, which enabled its significant improvement. This study is a part of project NCN 2014/15/B/ST10/00095 to JP, funded by Polish National Centre for Science. In Appendix we used the methods developed thanks to the project NCN 2011/01/B/ST10/06653.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
The effect of basaltic lava moving through the lithosphere on heat flow
Problem of thermal steady state of the lithosphere
The steady state is assumed in the numerous studies of thermal state of the lithosphere. A short discussion of this assumption is presented below.
If heat is transferred only by conduction then the temperature distribution is described by the following equation of the heat transfer (e.g. Czechowski 1993; Turcotte and Schubert 2001)
where t (s) is the time, T (K) is the temperature, c (J kg−1 K−1) is the specific heat at constant pressure, ρ (kg m−3) is the density, k (W m−1 K−1) is the coefficient of thermal conductivity (it could depend on the temperature T, pressure p and composition f), and Q (W m−3) is the rate of heat generation per unit volume.
Initially, the lithosphere, after formation as a result of magmatic processes, is not in thermal equilibrium (i.e. the time derivative in Eq. (5) is not zero). An analysis of the equation indicates that thermal equilibrium is asymptotically reached with the time scale:
where d is the characteristic spatial scale of the problem (e.g. the smallest dimension of the considered body) and κ (m2 s−1) = k/ρ c is the thermal diffusivity. After time τ the discrepancy between initial state and equilibrium decreases e = 2.7182… times, i.e. after time 2τ the discrepancy is ~ e2 times lower, i.e. ~ 14% of the initial discrepancy.
In Table 8, the time 2τ is given for different values of spatial characteristic dimension (e.g. the thickness of the considered region) and different values of the thermal conductivity. One can find that the upper 1 km layer is still not in the thermal equilibrium as a result of recent (i.e. ~ 15,000 years ago) ice regression. The crust (of 40 km thick) could be treated as a region of thermal equilibrium only ~ 100 Ma after formation or after later intensive magmatic activity.
Note, however, that the lithosphere is the basic unit in the global tectonics. The MOHO is just a chemical boundary, while the LAB is a mechanical and a thermal boundary. It means that in our research the whole lithosphere (crust and the rest of lithosphere) should be considered together. The time necessary for thermal equilibration of the continental lithosphere of 120 km thickness is of the order of 1 Gy. It means that many parts of the continental lithosphere are not in thermal equilibrium.
The 3D effects
Other problems result from assumption that models of the lithosphere are often 1D. It is justified in many regions where the lithosphere can be approximated as consisting of almost horizontal layers. In such a case, distributions of all parameters such as k and Q could be assumed to be one dimensional. The initial distribution of the temperature is usually unknown (it often cannot be approximated by 1D distribution) but for lithosphere older than 200 Ma the role of initial conditions is of less importance. The situation is different at the boundaries of two different units. If thermal properties of these units are different, the 2D or 3D models are necessary for the region spanning for the distance equal at least to two times the thickness of considered layers, e.g. ~ 100 km or more.
The three-dimensional distribution of temperature resulting from lava intrusion could be another reason for consideration of the 3D model. An example of such problem is presented below.
The effects of non-linearity of the equation
Most of parameters in Eq. (5) depend on the temperature: the specific heat at constant pressure c, the density ρ, the coefficient of thermal conductivity k (it could depend on the temperature, pressure and composition), and the rate of heat generation per unit volume Q. The dependence of c and ρ is rather of limited significance. The Q could be strongly nonlinear if phase transitions are considered (i.e. melting and solidification—see, e.g. Losiak et al. 2015). The dependence of k is important in any case if k changes substantially (e.g. Puziewicz et al. 2012). There are two consequences of this fact: (1) equation in simplified form with diffusivity term in the form k div grad(T) is not valid and (2) to obtain the true temperature profile the solution of equation is necessary (there are not simple methods without solution).
The three-dimensional time-dependent model
We present here a simple, time-dependent 3D model based on Eq. (5). The considered region is 60 × 60 × 70 km. The region consists of 1D horizontal layers in thermal equilibrium, i.e. the 1D distribution of temperature is initially assumed. The upper layer is 15 km thick with the rate of heat generation 6.67 × 10−10 W kg-1. The lower layer does not contain heat sources. The thermal conductivity is 3 W K−1 m−1. We simulate two magma intrusions at depth of 40–55 km, of size 20 × 40 × 15 km, consisting of 20% melt of basaltic composition during initial 2 Ma of simulation and 3rd intrusion 12 Ma after the initial one. This model is an approximation of geological conditions at the Jawor–Złotoryja Volcanic Complex described in the text of the paper.
The following boundary conditions are used:
at the upper boundary (isothermal): \({T^{\prime}_0}\) = 4 °C;
at the lower boundary: k ∂T/∂x = 34 mW m−2.
Adiabatic boundary conditions ∂T/∂x = 0 are assumed at the lateral boundaries.
The surfaces of constant temperature are presented in Figs. 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 for different times. The following colour scale for temperature is used (in °C): 10 °C = blue, 100 °C = pink, 500 °C = cyan, 750 °C = green, 950 °C = red. The regions of higher temperature are not depicted at presented figures. They are inside the red surface. The evolution of thermal conditions is presented in Figs. 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8. After period of the fast evolution (lasting a few Ma after an intrusion), the later evolution is rather slow. The surface effects (heat flow density) will last, however, for dozens of Ma.
Note, however, that the magnitude of the time-dependent effects depends on the magnitude of thermal intrusion averaged over considered region. If large initial temperature change concerns only a small part of the considered volume, then after averaging, the magnitude of the effect could be rather limited.
Rights and permissions
OpenAccess This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Puziewicz, J., Czechowski, L., Grad, M. et al. Crustal lithology vs. thermal state and Moho heat flow across the NE part of the European Variscan orogen: a case study from SW Poland. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 108, 673–692 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-018-01674-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-018-01674-7