Abstract
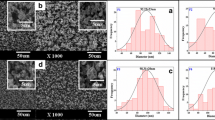
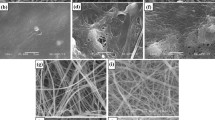
Chitosan/polyaniline nanofibers (CH/PANI) were prepared by an in situ oxidative polymerization of aniline in the presence of CH solution. An attractive development of nanofibers network provides free volume space for the easy encapsulation of drugs in the three-dimensional network structure. The CH/PANI hybrid was characterized by using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffractometry. Ketoprofen (KP), a model drug that contains a carboxylic group and a hydrophobic moiety, was loaded into CH/PANI hybrid. The release of KP from the hybrid was recorded in aqueous buffer solutions of pH 2, 6.7 and 7.4 simulating the case of oral administration. The release rate was found to be changing with the pH of the medium. The kinetics of the drug delivery system have been systematically studied by different models, which are commonly used, such as zero order, first order, Hixson–Crowell, Higuchi and Korsmeyer–Peppas models. The mechanism of release of the drug was found to follow the anomalous non-Fickian diffusion.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guimard NK, Gomez N, Schmidt CE (2007) Conducting polymers in biomedical engineering. Prog Polym Sci 32(8–9):876–921
Svirskis D, Travas-Sejdic J, Rodgers A, Garg S (2010) Electrochemically controlled drug delivery based on intrinsically conducting polymers. J Control Release 146:6–15
Salimian R, Shahrokhian S, Panahi S (2019) Enhanced electrochemical activity of hollow carbon sphere/polyaniline-based electrochemical biosensor for HBV DNA marker detection. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 5(5):2587–2594
Low LM, Seetharaman S, He KQ, Madou MJ (2000) Microactuators toward microvalves for responsive controlled drug delivery. Sens Actuator B Chem 67(1–2):149–160
Ayad MM, Salahuddin NA, Minisy IM, Amer WA (2014) Chitosan/polyaniline nanofibers coating on the quartz crystal microbalance electrode for gas sensing. Sens Actuator B Chem 202:144–153
Paul RB, Shuxi L, Alan GMD, Everaldo CV, Yen W, Peter IL (2006) Polyaniline, an electroactive polymer, supports adhesion and proliferation of cardiac myoblasts. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 17(1–2):199–212
Perez-Martinez CJ, Chávez SDM, del Castillo-Castro T, Ceniceros TEL, Castillo-Ortega MM, Rodríguez-Félix DE, Ruiz JCG (2016) Electroconductive nanocomposite hydrogel for pulsatile drug release. React Funct Polym 100:2–17
Brožová L, Holler P, Kovářová J, Stejskal J, Trchová M (2008) The stability of polyaniline in strongly alkaline or acidic aqueous media. Polym Degrad Stabil 93(3):592–600
Sahoo S, Sasmal A, Nanda R, Phani AR, Nayak PL (2010) Synthesis of chitosan–polycaprolactone blend for control delivery of ofloxacin drug. Carbohydr Polym 79:106–113
Patil SB, Inamdar SZ, Das KK, Akamanchi KG, Patil AV, Inamadar AC, Reddy KR, Raghu AV, Kulkarni RV (2020) Tailor-made electrically-responsive poly (acrylamide)-graft-pullulan copolymer based transdermal drug delivery systems: synthesis, characterization, in-vitro and ex-vivo evaluation. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 56:101525
Sedaghat S (2014) Synthesis and characterization of new biocompatible copolymer: chitosan-graft-polyaniline. Int Nano Lett 4(2):1–6
Li M, Guo Y, Wei Y, MacDiarmid AG, Lelkes PI (2006) Electrospinning polyaniline-contained gelatin nanofibers for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 27(13):2705–2715
Minisy IM, Salahuddine NA, Ayad MM (2019) Chitosan/polyaniline hybrid for the removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solutions. J Appl Polym Sci 136(6):47056
Shukla SK, Mishra AK, Arotiba OA, Mamba BB (2013) Chitosan-based nanomaterials: a state-of-the-art review. Int J Biol Macromol 59:46–55
Bernkop-Schnürch A, Dünnhaupt S (2012) Chitosan-based drug delivery systems. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 81(3):463–469
Hassani NA, Abdouss M, Faghihi S (2014) Synthesis and evaluation of PEG-O-chitosan nanoparticles for delivery of poor water soluble drugs: Ibuprofen. Mater Sci Eng C 41:91–99
Yazdani-Pedram M, Retuert J, Quijada R (2000) Hydrogels based on modified chitosan, 1. Synthesis and swelling behavior of poly(acrylic acid) grafted chitosan. Macromol Chem Phys 201(4):923–930
Krishna RK, Naidu B, Subha M, Sairam M, Aminabhavi TM (2006) Novel chitosan-based pH-sensitive interpenetrating network microgels for the controlled release of cefadroxil. Carbohydr Polym 66:333–344
Chen X, Song H, Fang T, Bai J, Xiong J, Ying H (2010) Preparation, characterization, and drug-release properties of pH/temperature-responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/chitosan semi-IPN hydrogel particles. J Appl Polym Sci 116:1342–1347
Risbud MV, Hardikar AA, Bhat SV, Bhonde RR (2000) pH-sensitive freeze-dried chitosan–polyvinyl pyrrolidone hydrogels as controlled release system for antibiotic delivery. J Control Release 68:23–30
Takeuchi H, Yamamoto H, Niwa T, Hino T, Kawashima Y (1996) Enteral absorption of insulin in rats from mucoadhesive chitosan-coated liposomes. Pharm Res 13(6):896–901
Kawashima Y, Yamamoto H, Takeuchi H, Kuno Y (2000) Mucoadhesive DL-lactide/glycolide copolymer nanospheres coated with chitosan to improve oral delivery of elcatonin. Pharm Dev Technol 5(1):77–85
Gupta CR, Kishore GK, Ratna JV (2013) Development and evaluation of aceclofenac matrix tablets using polyethylene oxides as sustained release polymers. J Pharm Res 6(2):249–254
Moutsatsou P, Coopman K, Georgiadou S (2017) Biocompatibility assessment of conducting PANI/chitosan nanofibers for wound healing applications. Polymers 9(12):687
Kantor TG (1986) Ketoprofen: a review of its pharmacologic and clinical properties. Pharmacotherapy 6(3):93–103
Macocinschi D, Filip D, Vlad S, Oprea AM, Gafitanu CA (2012) Characterization of a poly(ether urethane)-based controlled release membrane system for delivery of ketoprofen. Appl Surf Sci 259:416–423
Ayad MM, Salahuddin NA, Torad NL, El-Nasr A (2016) pH-responsive sulphonated mesoporous silica: a comparative drug release study. RSC Adv 6:57929–57940
Lin H, Zhu G, Xing J, Gao B, Qiu S (2009) Polymer−mesoporous silica materials templated with an oppositely charged surfactant/polymer system for drug delivery. Langmuir 25:10159–10164
Kulkarni PV, Roney CA, Antich PP, Bonte FJ, Raghu AV, Aminabhavi TM (2010) Quinoline-n-butylcyanoacrylate-based nanoparticles for brain targeting for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 2(1):35–47
Han MG, Cho SK, Oh SG, Im SS (2002) Preparation and characterization of polyaniline nanoparticles synthesized from DBSA micellar solution. Synth Met 126:53–60
Ismail YA, Shin SR, Shin KM, Yoon SG, Shon K, Kim SI, Kim SJ (2008) Electrochemical actuation in chitosan/polyaniline microfibers for artificial muscles fabricated using an in situ polymerization. Sens Actuator B Chem 129(2):834–840
Osman Z, Arof AK (2003) FTIR studies of chitosan acetate based polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 48:993–999
Ma G, Yang D, Zhou Y, Xiao M, Kennedy JF, Nie J (2008) Preparation and characterization of water-soluble N-alkylated chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 74(1):121–126
Suhas DP, Aminabhavi TM, Raghu AV (2014) para-Toluene sulfonic acid treated clay loaded sodium alginate membranes for enhanced pervaporative dehydration of isopropanol. Appl Clay Sci 101:419–429
Suhas DP, Raghu AV, Jeong HM, Aminabhavi TM (2013) Graphene-loaded sodium alginate nanocomposite membranes with enhanced isopropanol dehydration performance via a pervaporation technique. RSC Adv 3(38):17120–17130
Ràfols C, Rosés M, Bosch E (1997) A comparison between different approaches to estimate the aqueous pKa values of several non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Anal Chim Acta 338(1–2):127–134
Kalam MA, Humayun M, Parvez N, Yadav S, Garg A, Amin S, Sultana Y, Ali A (2007) Release kinetics of modified pharmaceutical dosage forms: a review. Cont J Pharm Sci 1:30–35
Wagner JG (1967) Interpretation of percent dissolved–time plots derived from In vitro testing of conventional tablets and capsules. J Pharm Sci 58:1253–1257
Higuchi T (1963) Mechanism of sustained-action medication theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J Pharm Sci 52:1145–1149
Hixson AW, Crowell JH (1931) Dependence of reaction velocity upon surface and agitation. Ind Eng Chem 23(10):1160–1168
Korsmeyer RW, Peppas NA (1983) Solute and penetrant diffusion in swellable polymers. J Control Release 1:89–98
Acknowledgements
This work was done in the Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, University of Tanta, without sources of financial funding and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IMM contributed to methodology, data curation, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing. NAS contributed to supervision, validation, and writing—review and editing. MMA contributed to supervision, conceptualization, validation, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minisy, I.M., Salahuddin, N.A. & Ayad, M.M. In vitro release study of ketoprofen-loaded chitosan/polyaniline nanofibers. Polym. Bull. 78, 5609–5622 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03385-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03385-z