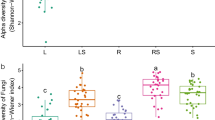
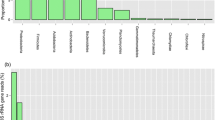
Abstract
Microbial bioremediation of heavy metal–contaminated soil is a potential technique to reduce heavy metals in crop plants. However, the dynamics and roles of the local microbiota in bioremediation of heavy metal–contaminated soil following microbial application are rarely reported. In this study, we used Pseudomonas chenduensis strain MBR for bioremediation of Cd-contaminated paddy soil and investigated its effects on the dynamics of the local soil bacterial community and Cd accumulation in rice. Cd accumulation in rice grains and roots were significantly reduced by the addition of the strain MBR. The addition of the strain MBR caused greater changes in bacterial communities in rhizosphere soil than in bulk soil. MBR enhanced the roles of microbial communities in transformation of Cd fractions, especially in rhizosphere soil. The strain MBR likely regulated abundant subcommunities more than rare subcommunities to improve Cd bioremediation, especially in rhizosphere soil. Consequently, the dynamics and functional roles of the local microbial communities differed significantly during bioremediation between abundant and rare subcommunities and between rhizosphere soil and bulk soil. This study provides new insight into the microbiota-related mechanisms underlying bioremediation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadipour F, Bahramifar N, Mahmood Ghasempouri S (2015) Fractionation and mobility of cadmium and lead in soils of Amol area in Iran, using the modified BCR sequential extraction method. Chem Speciat Bioavailab 26(1):31–36
Azimi A, Azari A, Rezakazemi M, Ansarpour M (2017) Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters: a review. ChemBioEng Rev 4(1):37–59
Bais HP, Weir TL, Perry LG, Gilroy S, Vivanco JM (2006) The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:233–266
Batista MB, Teixeira CS, Sfeir MZT, Alves LPS, Valdameri G, Pedrosa FO, Sassaki GL, Steffens MBR, de Souza EM, Dixon R, Muller-Santos M (2018) PHB biosynthesis counteracts redox stress in Herbaspirillum seropedicae. Front Microbiol 9:472
Chen L, Luo S, Li X, Wan Y, Chen J, Liu C (2014) Interaction of Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. and functional endophyte Pseudomonas sp. Lk9 on soil heavy metals uptake. Soil Biol Biochem 68:300–308
Chen D, Guo H, Li RY, Li LQ, Pan GX, Chang A, Joseph S (2016) Low uptake affinity cultivars with biochar to tackle Cd-tainted rice - a field study over four rice seasons in Hunan, China. Sci Total Environ 541:1489–1498
Cottrell MT, David KL (2003) Contribution of major bacterial groups to bacterial biomass production (thymidine and leucine incorporation) in the Delaware estuary. Limnol Oceanogr 48(1):168–178
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Giaramida L, Reich PB, Khachane AN, Hamonts K, Edwards C, Lawton LA, Singh BK (2016) Lack of functional redundancy in the relationship between microbial diversity and ecosystem functioning. J Ecol 104(4):936–946
Dell’Anno A, Beolchini F, Rocchetti L, Luna GM, Danavaro R (2012) High bacterial biodiversity increases degradation performance of hydrocarbons during bioremediation of contaminated harbor marine sediments. Environ Pollut 167:85–92
Fuentes S, Mendez V, Aguila P, Seeger M (2014) Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons: catabolic genes, microbial communities, and applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(11):4781–4794
Hou D, Wang R, Gao X, Wang K, Lin Z, Ge J, Liu T, Wei S, Chen W, Xie R (2018) Cultivar-specific response of bacterial community to cadmium contamination in the rhizosphere of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Pollut 241:63–73
Huang D, Xue W, Zeng G, Wan J, Chen G, Huang C, Zhang C, Cheng M, Xu P (2016) Immobilization of Cd in river sediments by sodium alginate modified nanoscale zero-valent iron: impact on enzyme activities and microbial community diversity. Water Res 106:15–25
Huang D, Liu L, Zeng G, Xu P, Huang C, Deng L, Wang R, Wan J (2017) The effects of rice straw biochar on indigenous microbial community and enzymes activity in heavy metal-contaminated sediment. Chemosphere 174:545–553
Ingwersen J, Streck T (2005) A regional-scale study on the crop uptake of cadmium from sandy soils. J Environ Qual 34(3):1026–1035
Jamali MK, Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Arain MB, Jalbani N, Memon AR (2007) Speciation of heavy metals in untreated domestic wastewater sludge by time saving BCR sequential extraction method. J Environ Sci Health A 42(5):649–659
Jia X, Dini-Andreote F, Salles JF (2018) Community assembly processes of the microbial rare biosphere. Trends Microbiol 26(9):738–747
Jiao S, Chen W, Wei G (2017a) Biogeography and ecological diversity patterns of rare and abundant bacteria in oil-contaminated soils. Mol Ecol 26(19):5305–5317
Jiao S, Luo Y, Lu M, Xiao X, Lin Y, Chen W, Wei G (2017b) Distinct succession patterns of abundant and rare bacteria in temporal microcosms with pollutants. Environ Pollut 225:497–505
Jousset A, Bienhold C, Chatzinotas A, Gallien L, Gobet A, Kurm V, Küsel K, Rillig MC, Rivett DW, Salles JF (2017) Where less may be more: how the rare biosphere pulls ecosystems strings. ISME J 11(4):853–862
Kou Y, Li J, Wang Y, Li C, Tu B, Yao M, Li X (2017) Scale-dependent key drivers controlling methane oxidation potential in Chinese grassland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 111:104–114
Li H, Luo N, Li YW, Cai QY, Li HY, Mo CH, Wong MH (2017) Cadmium in rice: Transport mechanisms, influencing factors, and minimizing measures. Environ Pollut 224:622–630
Li L, Wang S, Li X, Li T, He X, Tao Y (2018) Effects of Pseudomonas chenduensis and biochar on cadmium availability and microbial community in the paddy soil. Sci Total Environ 640-641:1034–1043
Lin Q, De Vrieze J, Li J, Li X (2016) Temperature affects microbial abundance, activity and interactions in anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 209:228–236
Lynch MD, Neufeld JD (2015) Ecology and exploration of the rare biosphere. Nat Rev Microbiol 13(4):217–229
Mo Y, Zhang W, Yang J, Lin Y, Yu Z, Lin S (2018) Biogeographic patterns of abundant and rare bacterioplankton in three subtropical bays resulting from selective and neutral processes. ISME J 12(9):2198–2210
Muehe EM, Weigold P, Adaktylou IJ, Planer-Friedrich B, Kraemer U, Kappler A, Behrens S (2015) Rhizosphere microbial community composition affects cadmium and zinc uptake by the metal-hyperaccumulating plant Arabidopsis halleri. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(6):2173–2181
Pester M, Bittner N, Deevong P, Wagner M, Loy A (2010) A ‘rare biosphere’ microorganism contributes to sulfate reduction in a peatland. ISME J 4(12):1591–1602
Philippot L, Raaijmakers JM, Lemanceau P, van der Putten WH (2013) Going back to the roots: the microbial ecology of the rhizosphere. Nat Rev Microbiol 11(11):789–799
Pianka ER (1970) On r-and K-selection. Am Nat 104(940):592–597
Qian JW, Tao Y, Zhang WJ, He XH, Gao P, Li DP (2013) Presence of Fe3+ and Zn2+ promoted biotransformation of Cd-citrate complex and removal of metals from solutions. J Hazard Mater 263(Pt 2):367–373
Rivett DW, Bell T (2018) Abundance determines the functional role of bacterial phylotypes in complex communities. Nat Microbiol 3(7):767–772
Shu D, Zhang B, He Y, Wei G (2018) Abundant and rare microbial sub-communities in anammox granules present contrasting assemblage patterns and metabolic functions in response to inorganic carbon stresses. Bioresour Technol 265:299–309
Siripornadulsil S, Siripornadulsil W (2013) Cadmium-tolerant bacteria reduce the uptake of cadmium in rice: potential for microbial bioremediation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 94:94–103
Soman C, Li D, Wander MM, Kent AD (2016) Long-term fertilizer and crop-rotation treatments differentially affect soil bacterial community structure. Plant Soil 413(1-2):145–159
Suksabye P, Pimthong A, Dhurakit P, Mekvichitsaeng P, Thiravetyan P (2016) Effect of biochars and microorganisms on cadmium accumulation in rice grains grown in Cd-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(2):962–973
Tao Y, Zhou Y, He X, Hu X, Li D (2014) Pseudomonas chengduensis sp. nov., isolated from landfill leachate. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64(Pt 1):95–100
Wang Y, Wang SR, Luo CL, Xu Y, Pan SH, Li J, Ming LL, Zhang G, Li XD (2015) Influence of rice growth on the fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a subtropical paddy field: a life cycle study. Chemosphere 119:1233–1239
Xiong T, Yuan X, Wang H, Leng L, Li H, Wu Z, Jiang L, Xu R, Zeng G (2017) Implication of graphene oxide in Cd-contaminated soil: a case study of bacterial communities. J Environ Manag 205:99–106
Xu Y, Seshadri B, Sarkar B, Wang H, Rumpel C, Sparks D, Farrell M, Hall T, Yang X, Bolan N (2017a) Biochar modulates heavy metal toxicity and improves microbial carbon use efficiency in soil. Sci Total Environ 621:148–159
Xu ZM, Li QS, Yang P, Ye HJ, Chen ZS, Guo SH, Wang LL, He BY, Zeng EY (2017b) Impact of osmoregulation on the differences in Cd accumulation between two contrasting edible amaranth cultivars grown on Cd-polluted saline soils. Environ Pollut 224:89–97
Yan W, Ma H, Shi G, Li Y, Sun B, Xiao X, Zhang Y (2017) Independent shifts of abundant and rare bacterial populations across East Antarctica Glacial Foreland. Front Microbiol 8:1534
Yu HY, Liu C, Zhu J, Li F, Deng DM, Wang Q, Liu C (2016) Cadmium availability in rice paddy fields from a mining area: the effects of soil properties highlighting iron fractions and pH value. Environ Pollut 209:38–45
Zhang Z, Solaiman ZM, Meney K, Murphy DV, Rengel Z (2012) Biochars immobilize soil cadmium, but do not improve growth of emergent wetland species Juncus subsecundus in cadmium-contaminated soil. J Soils Sediments 13(1):140–151
Funding
The study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0800702) and the Open Foundation Project of Key Laboratory of Environmental and Applied Microbiology, CAS (KLCAS-2018-4), Sichuan Key Research and Development Program (2017SZ0184), and China Biodiversity Observation Networks (Sino BON).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lingjuan Li (LL) and Qiang Lin (QL) performed the experiments, analyzed the results, and wrote the manuscript. Yong Tao (YT) conceived and designed the study, as well as revised the manuscript. Xiangzhen Li (XL) revised the manuscript. Tiezhu Li (TL), Xiaohong He (XH), and Daping Li (DL) participated in the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 568 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Lin, Q., Li, X. et al. Dynamics and potential roles of abundant and rare subcommunities in the bioremediation of cadmium-contaminated paddy soil by Pseudomonas chenduensis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 8203–8214 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10059-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10059-y