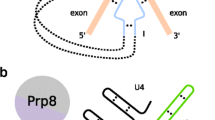
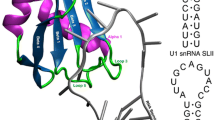
Abstract
Trans-splicing is a process by which 5′- and 3′-ends of two pre-RNA molecules transcribed from different sites of the genome can be joined together to form a single RNA molecule. The spliced leader (SL) trans-splicing is mediated by the spliceosome and it allows the replacement of 5′-end of pre-mRNA by 5′(SL)-end of SL-RNA. This form of splicing has been observed in many phylogenetically unrelated eukaryotes. Either the SL trans-splicing (SLTS) originated in the last eukaryotic common ancestor (LECA) (or even earlier) and it was lost in most eukaryotic lineages, or this mechanism of RNA processing evolved several times independently in various unrelated eukaryotic taxa. The bioinformatic comparisons of SL-RNAs from various eukaryotic taxonomic groups have revealed the similarities of secondary structures of most SL-RNAs and a relative conservation of their splice sites (SSs) and Sm-binding sites (SmBSs). We propose that such structural and functional similarities of SL-RNAs are unlikely to have evolved repeatedly many times. Hence, we favor the scenario of an early evolutionary origin for the SLTS and multiple losses of SL-RNAs in various eukaryotic lineages.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LECA:
-
The last eukaryotic common ancestor
- LUCA:
-
The last universal common ancestor
- Sm:
-
“Smith antigen” proteins which bind to small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), i.e., spliceosomal U (U-rich) or SL snRNAs
- SmBS:
-
Sm-binding site
- SL:
-
Capped spliced leader sequence which is transferred to 5′-end of pre-mRNA during SL trans-splicing
- SL-RNA:
-
Spliced leader (SL) snRNA which serves as donor of capped SL sequences for pre-mRNA
- SLTS:
-
Spliced leader trans-splicing
- SS:
-
Splice site
References
Allen MA, Hillier LW, Waterston RH, Blumenthal T (2011) A global analysis of C. elegans trans-splicing. Genome Res 21:255–264
Bangs JD, Crain PF, Hashizume T, McCloskey JA, Boothroyd JC (1992) Mass spectrometry of mRNA cap 4 from trypanosomatids reveals two novel nucleosides. J Biol Chem 267:9805–9815
Bartschat S, Samuelsson T (2010) U12 type introns were lost at multiple occasions during evolution. BMC Genom 11:106
Beauparlant MA, Drouin G (2014) Multiple independent insertions of 5S rRNA genes in the spliced-leader gene family of trypanosome species. Curr Genet 60:17–24
Berriman M, Ghedin E, Hertz-Fowler C et al (2005) The genome of the african trypanosome Trypanosoma brucei. Science 309:416–422
Bitar M, Boroni M, Macedo AM, Machado CR, Franco GR (2013) The spliced leader trans-splicing mechanism in different organisms: molecular details and possible biological roles. Front Genet 4:199
Blaxter M, Liu L (1996) Nematode spliced leaders—ubiquity, evolution and utility. Int J Parasitol 26:1025–1033
Blumenthal T (2004) Operons in eukaryotes. Brief Funct Genomic Proteom 3:199–211
Blumenthal T (2012) Trans-splicing and operons in C. elegans. WormBook. 2012 Nov 20:1–11. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.5.2
Blumenthal T, Davis P,Garrido-Lecca A (2015) Operon and non-operon gene clusters in the C. elegans genome (April 28, 2015). WormBook, ed. The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook, doi/10.1895/wormbook.1.175.1, http://www.wormbook.org
Brehm K, Jensen K, Frosch M (2000) mRNA trans-splicing in the human parasitic cestode Echinococcus multilocularis. J Biol Chem 275:38311–38318
Bruzik JP, Steitz JA (1990) Spliced leader RNA sequences can substitute for the essential 5′ end of U1 RNA during splicing in a mammalian in vitro system. Cell 62:889–899
Bruzik JP, Doren KV, Hirsh D, Steitz JA (1988) Trans splicing involves a novel form of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Nature 335:559–562
Campbell DA, Thomas S, Sturm NR (2003) Transcription in kinetoplastid protozoa: why be normal? Microbes Infect 5:1231–1240
Darty K, Denise A, Ponty Y (2009) VARNA: Interactive drawing and editing of the RNA secondary structure. Bioinformatics 25:1974–1975
Davis RE (1996) Spliced leader RNA trans-splicing in metazoa. Parasitol Today 12:33–40
Davis RE (1997) Surprising diversity and distribution of spliced leader RNAs in flatworms. Mol Biochem Parasitol 87:29–48
Davis RE, Hardwick C, Tavernier P, Hodgson S, Singh H (1995) RNA Trans-splicing in flatworms. Analysis of trans-spliced mRNAs and genes in the human parasite Schistosoma mansoni. J Biol Chem 270:21813–21819
Denker JA, Zuckerman DM, Maroney PA, Nilsen TW (2002) New components of the spliced leader RNP required for nematode trans-splicing. Nature 417:667–670
Derelle R, Momose T, Manuel M, Da Silva C, Wincker P, Houliston E (2010) Convergent origins and rapid evolution of spliced leader trans-splicing in Metazoa: Insights from the Ctenophora and Hydrozoa. RNA 16:696–707
Doren KV, Hirsh D (1988) Trans-spliced leader RNA exists as small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 335:556–559
Douris V, Telford MJ, Averof M (2010) Evidence for multiple independent origins of trans-splicing in Metazoa. Mol Biol Evol 27:684–693
Drouin G, Tsang C (2012) 5S rRNA gene arrangements in protists: a case of nonadaptive evolution. J Mol Evol 74:342–351
Ebel C, Frantz C, Paulus F, Imbault P (1999) Trans-splicing and cis-splicing in the colourless Euglenoid, Entosiphon sulcatum. Curr Genet 35:542–550
Evans D, Blumenthal T (2000) trans splicing of polycistronic Caenorhabditis elegans pre-mRNAs: analysis of the SL2 RNA. Mol Cell Biol 20:6659–6667
Evans D, Zorio D, MacMorris M, Winter CE, Lea K, Blumenthal T (1997) Operons and SL2 trans-splicing exist in nematodes outside the genus Caenorhabditis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9751–9756
Ganot P, Kallesøe T, Reinhardt R, Chourrout D, Thompson EM (2004) Spliced-leader RNA trans splicing in a chordate, Oikopleura dioica, with a compact genome. Mol Cell Biol 24:7795–7805
Gibson W, Bingle L, Blendeman W, Brown J, Wood J, Stevens J (2000) Structure and sequence variation of the trypanosome spliced leader transcript. Mol Biochem Parasitol 107:269–277
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hannon GJ, Maroney PA, Nilsen TW (1991) U small nuclear ribonucleoprotein requirements for nematode cis- and trans-splicing in vitro. J Biol Chem 266:22792–22795
Harris KA, Crothers DM, Ullu E (1995) In vivo structural analysis of spliced leader RNAs in Trypanosoma brucei and Leptomonas collosoma: a flexible structure that is independent of cap4 methylations. RNA 1:351–362
Harrison N, Kalbfleisch A, Connolly B, Pettitt J, Müller B (2010) SL2-like spliced leader RNAs in the basal nematode Prionchulus punctatus: New insight into the evolution of nematode SL2 RNAs. RNA 16:1500–15007
Hastings KEM (2005) SL trans-splicing: easy come or easy go? Trends Genet 21:240–247
Hofacker IL, Fekete M, Stadler PF (2002) Secondary structure prediction for aligned RNA sequences. J Mol Biol 319:1059–1066
Kim S, Bachvaroff TR, Handy SM, Delwiche CF (2011) Dynamics of actin evolution in dinoflagellates. Mol Biol Evol 28:1469–1480
Koehl P (2001) Protein structure similarities. Curr Opinion Struct Biol 11:348–353
Lasda EL, Blumenthal T (2011) Trans-splicing. Wiley Interdiscip Rev. RNA 2:417–434
LeCuyer KA, Crothers DM (1993) The Leptomonas collosoma spliced leader RNA can switch between two alternate structural forms. Biochemistry 32:5301–5311
Liang XH, Haritan A, Uliel S, Michaeli S (2003) trans and cis splicing in trypanosomatids: mechanism, factors, and regulation. Eukaryot Cell 2:830–840
Lidie KB, van Dolah FM (2007) Spliced leader RNA-mediated trans-splicing in a dinoflagellate, Karenia brevis. J Eukaryot Microbiol 54:427–435
Lin CF, Mount SM, Jarmołowski A, Makałowski W (2010) Evolutionary dynamics of U12-type spliceosomal introns. BMC Evol Biol 10:47
Lorenz R, Bernhart S, Honer zu Siederdissen C, Tafer H, Flamm C, Stadler P, Hofacker I (2011) ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol Biol 6:26
Marlétaz F, Gilles A, Caubit X, Perez Y, Dossat C, Samain S, Gyapay G, Wincker P, Le Parco Y (2008) Chaetognath transcriptome reveals ancestral and unique features among bilaterians. Genome Biol 9:R94
Maroney PA, Hannon GJ, Shambaugh JD, Nilsen TW (1991) Intramolecular base pairing between the nematode spliced leader and its 5′ splice site is not essential for trans-splicing in vitro. EMBO J 10:3869–3875
Maroney PA, Denker JA, Darzynkiewicz E, Laneve R, Nilsen TW (1995) Most mRNAs in the nematode Ascaris lumbricoides are trans-spliced: a role for spliced leader addition in translational efficiency. RNA 1:714–723
Maroney PA, Yu YT, Jankowska M, Nilsen TW (1996) Direct analysis of nematode cis- and trans-spliceosomes: a functional role for U5 snRNA in spliced leader addition trans-splicing and the identification of novel Sm snRNPs. RNA 2:735–745
Marz M, Vanzo N, Stadler PF (2010) Temperature-dependent structural variability of RNAs: spliced leader RNAs and their evolutionary history. J Bioinf Comput Biol 8:1–17
Mateášiková-Kováčová B, Vesteg M, Drahovská H, Záhonová K, Vacula R, Krajčovič J (2012) Nucleus-encoded mRNAs for chloroplast proteins GapA, PetA, and PsbO are trans-spliced in the flagellate Euglena gracilis irrespective of light and plastid function. J Eukaryot Microbiol 59:651–653
Matera AG, Wang Z (2014) A day in the life of the spliceosome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:108–121
Miller SI, Landfear SM, Wirth DF (1986) Cloning and characterization of a Leishmania gene encoding a RNA spliced leader sequence. Nucl Acids Res 14:7341–7360
Muhich ML, Hughes DE, Simpson AM, Simpson L (1987) The monogenetic kinetoplastid protozoan, Crithidia fasciculata, contains a transcriptionally active, multicopy mini-exon sequence. Nucl Acids Res 15:3141–3153
Nilsen TW (1993) Trans-splicing of nematode premessenger RNA. Annu Rev Microbiol 47:413–440
Nilsen TW (1995) trans-splicing: an update. Mol Biochem Parasitol 73:1–6
Nilsen TW (2001) Evolutionary origin of SL-addition trans-splicing: still an enigma. Trends Genet 17:678–680
Nowack ECM, Price DC, Bhattacharya D, Singer A, Melkonian M, Grossman AR (2016) Gene transfers from diverse bacteria compensate for reductive genome evolution in the chromatophore of Paulinella chromatophora. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:12214–12219
Palfi Z, Schimanski B, Güntze A, Lücke S, Bindereif A (2005) U1 small nuclear RNP from Trypanosoma brucei: a minimal U1 snRNA with unusual protein components. Nucl Acids Res 8:2493–2503
Pouchkina-Stantcheva NN, Tunnacliffe A (2005) Spliced leader RNA-mediated trans-splicing in phylum Rotifera. Mol Biol Evol 22:1482–1489
Protasio AV, Tsai IJ, Babbage A et al (2012) A systematically improved high quality genome and transcriptome of the human blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 6:e1455
Rajkovic A, Davis RE, Simonsen JN, Rottman FM (1990) A spliced leader is present on a subset of mRNAs from the human parasite Schistosoma mansoni. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:8879–8883
Rossi A, Ross EJ, Jack A, Sánchez Alvarado A (2014) Molecular cloning and characterization of SL3: a stem cell-specific SL RNA from the planarian Schmidtea mediterranea. Gene 533:156–167
Roy SW (2017) Genomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals spliced leader trans-splicing in cryptomonads. Genome Biol Evol 9:468–473
Russell AG, Charette JM, Spencer DF, Gray MW (2006) An early evolutionary origin for the minor spliceosome. Nature 443:863–866
Siebert S, Backofen R (2005) MARNA: multiple alignment and consensus structure prediction of RNAs based on sequence structure comparisons. Bioinformatics 21:3352–3359
Siegel TN, Hekstra DR, Wang X, Dewell S, Cross GAM (2010) Genome-wide analysis of mRNA abundance in two life-cycle stages of Trypanosoma brucei and identification of splicing and polyadenylation sites. Nucl Acids Res 38:4946–4957
Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, Lopez R, McWilliam H, Remmert M, Söding J, Thompson JD, Higgins DG (2011) Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol 7:539
Stover NA, Steele RE (2001) Trans-spliced leader addition to mRNAs in a cnidarian. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:5693–5698
Stover NA, Kaye MS, Cavalcanti ARO (2006) Spliced leader trans-splicing. Curr Biol 16:R8–R9
Sturm NR, Yu MC, Campbell DA (1999) Transcription termination and 3′-end processing of the spliced leader RNA in kinetoplastids. Mol Cell Biol 19:1595–1604
Thomas JD, Conrad RC, Blumenthal T (1988) The C. elegans trans-spliced leader RNA is bound to Sm and has a trimethylguanosine cap. Cell 54:533–539
Torarinsson E, Lindgreen S (2008) WAR: Webserver for aligning structural RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W79–W84
Van Doren K, Hirsh D (1990) mRNAs that mature through trans-splicing in Caenorhabditis elegans have a trimethylguanosine cap at their 5′ termini. Mol Cell Biol 10:1769–1772
Vesteg M, Krajčovič J (2011) The falsifiability of the models for the origin of eukaryotes. Curr Genet 57:367–390
Vesteg M, Vacula R, Burey S, Löffelhardt W, Drahovská H, Martin W, Krajčovič J (2009) Expression of nucleus-encoded genes for chloroplast proteins in the flagellate Euglena gracilis. J Eukaryot Microbiol 56:159–166
Vesteg M, Vacula R, Steiner JM, Mateášiková B, Löffelhardt W, Brejová B, Krajčovič J (2010) A possible role for short introns in the acquisition of stroma-targeting peptides in the flagellate Euglena gracilis. DNA Res 17:223–231
Vesteg M, Šándorová Z, Krajčovič J (2012) Selective forces for the origin of spliceosomes. J Mol Evol 74:226–231
Waterhouse AM, Procter JB, Martin DMA, Clamp M, Barton GJ (2009) Jalview Version 2–a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 25:1189–1191
Yang F, Xu D, Zhuang Y et al (2015) Spliced leader RNA trans-splicing discovered in copepods. Sci Rep 5:17411
Yeats B, Matsumoto J, Mortimer SI, Shoguchi E, Satoh N, Hastings KE (2010) SL RNA genes of the ascidian tunicates Ciona intestinalis and Ciona savignyi. Zool Sci 27:171–180
Yu YT, Maroney PA, Nilsen TW (1993) Functional reconstitution of U6 snRNA in nematode cis- and trans-splicing: u6 can serve as both a branch acceptor and a 5′ exon. Cell 75:1049–1059
Zayas RM, Bold TD, Newmark PA (2005) Spliced-leader trans-splicing in freshwater planarians. Mol Biol Evol 22:2048–2054
Zhang H, Hou Y, Miranda L, Campbell DA, Sturm NR, Gaasterland T, Lin S (2007) Spliced leader RNA trans-splicing in dinoflagellates. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 104:4618–4623
Zhang H, Campbell DA, Sturm NR, Lin S (2009) Dinoflagellate spliced leader RNA genes display a variety of sequences and genomic arrangements. Mol Biol Evol 26:1757–1771
Zhang H, Campbell DA, Sturm NR, Dungan CF, Lin S (2011) Spliced leader RNAs, mitochondrial gene frameshifts and multi-protein phylogeny expand support for the genus Perkinsus as a unique group of alveolates. PLoS ONE 6:e19933
Zuker M (2003) Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucl Acids Res 31:3406–3415
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Scientific Grant Agency of the Slovak Ministry of Education and the Academy of Sciences (Grants VEGA 1/0626/13 and 1/0535/17), and by project ITMS 26210120024 supported by the Research & Development Operational Programme funded by the ERDF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krchňáková, Z., Krajčovič, J. & Vesteg, M. On the Possibility of an Early Evolutionary Origin for the Spliced Leader Trans-Splicing. J Mol Evol 85, 37–45 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-017-9803-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-017-9803-y