Abstract
Aortal valve mineralization very frequently causes a genesis of aortic stenosis, which is the most often surgically treated heart disease. Hydroxyapatite deposits have been identified as one of the causes leading to the loss of elasticity of the aortic valves. It is known that phosphates/calcium is accumulated in valve tissues during mineralization, but the mechanism of this process remains unclear. The work is focused mainly on the study of protein composition of mineralized aortic valves by nano-liquid chromatography electrospray ionization in a quadrupole orthogonal acceleration time-of-flight mass spectrometry. New methodological approach based on direct enzymatic digestion of proteins contained in hydroxyapatite deposits was developed for the study of pathological processes connected with osteogenesis. Our objectives were to simplify the traditional analytical protocols of sample preparation and to analyze the organic components of the explanted aortic valves for significant degenerative aortic stenosis. The study of aortic valve mineralization on the molecular level should contribute to understanding this process, which should consequently lead to effective prevention as well as to new ways of treatment of this grave disease.

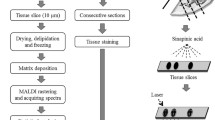
The photo of explanted calcification of human aortal valve.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajamannan NM (2004) Is it time for medical therapy for aortic valve disease? Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2(6):845–854
Rosenhek R, Rader F, Loho N, Gabriel H, Heger M, Klaar U, Schemper M, Binder T, Maurer G, Baumgartner H (2004) Statins but not angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors delay progression of aortic stenosis. Circulation 110(10):1291–1295
Antonini-Canterin F, Popescu BA, Huang G, Korcova-Miertusova R, Rivaben D, Faggiano P, Pavan D, Piazza R, Bolis A, Ciavattone A, Ruggiero A, Nicolosi GL (2005) Progression of aortic valve sclerosis and aortic valve stenosis: what is the role of statin treatment? Ital Heart J 6(2):119–124
Borer JS (2005) Aortic stenosis and statins: more evidence of “pleotrophy”? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(3):476–477
Peltier M, Enriquez-Sarano M, Slama M, Tribouilloy C (2004) New concepts on the physiopathology and therapy of aortic stenosis. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss 97(4):327–332
David TE, Ivanov JI (2003) Is degenerative calcification of native aortic valve similar to calcification of bioprosthetic heart valves? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 126:939–941
Rajamannan NM, Sangiorgi G, Springett M, Arnold K, Mohacsi T, Spagnoli LG, Edwards WD, Tajik AJ, Schwartz RS (2001) Experimental hypercholesterolemia induces apoptosis in aortic valve. J Heart Valve Dis 10:371–374
Helske S, Kupari M, Lindstedt KA, Kovanen PY (2007) Aortic valve stenosis: an active atheroinflammatory process. Curr Opin Lipidol 18:483–491
Olsson M, Thyberg J, Nilsson J (1999) Presence of oxidized low density lipoprotein in nonrheumatic stenotic aortic valves. Arterioscler Tromb Vasc Biol 19:1218–1222
Fusaro M, Crepaldi G, Maggi S, Galli F, D'Angelo A, Calo L, Giannini S, Miozzo D, Gallieni M (2010) Vitamin K, bone fractures, and vascular calcifications in chronic kidney disease: an important but poorly studied relationship. J Endocrinol Investig 34(4):317–323
Hsu JJ, Tintut Y, Demer LL (2008) Vitamin D and osteogenic differentiation in the artery wall. CJASN 3:1542–1547
Hass GM, Landerholm W, Hemmens A (1966) A production of calcific athero-arteriosclerosis and thromboarteritis with nicotine, vitamin D and dietary cholesterol. Am J Pathol 49:739–771
Rajamannan NM, Subramaniam M, Springett M, Sebo TC, Niekrasz M, McConnell JP, Singh RJ, Stone NJ, Bonow RO, Spelsberg TC (2002) Atorvastatin inhibits hypercholesterolemia-induced cellular proliferation and bone matrix production in the rabbit aortic valve. Circulation 105(22):2660–2665
Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, Murad MH, Weaver CM (2011) Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:1911–1930
Liu LB, Taylor CB, Peng SK, Mikkelson B (1979) Experimental arteriosclerosis in Rhesus monkeys induced by multiple risk factors: cholesterol, vitamin D, and nicotine. Paroi Arterielle 5:25–37
Brooks CJW, Harland WA, Steel G (1966) Squalene, 26-hydroxycholesterol and 7-ketocholesterol in human atheromatous plaques. Biochim Biophys Acta 125:620–622
Lewis RW (1975) The squalene content of atheromatous plaques. A re-examination. Atherosclerosis 22:637–640
Johnson RC, Leopold JA, Loscalzo J (2006) Vascular calcification pathobiological mechanisms and clinical implications. Circ Res 99:1044–1059
Voet D, Voet JG (2004) Biochemistry, volume 1: biomolecules, mechanisms of enzyme action, and metabolism, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 663–664
Howard HT, Hsu AA, Maria T (2008) Induction of calcification by serum depletion in cell culture: a model for focal calcification in aortas related to atherosclerosis. Lipids Health Dis 7:2
Symon K. Obecná a komunální hygiena. Učebnice pro lékařské fakulty (pro posluchače Lékařské fakulty hygienické). Avicenum, Praha 1982
Brázda O (2008) Sláva a pád jedné preventivní metody. Medical Tribune C7
Strunecká A, Patočka J (2003) Structure and bonding. In: Atwood D, Roesky C (eds) New developments in biological aluminum chemistry—book 2. Springer, Berlin, pp 139–181, 104
Kumar R (1991) Vitamin D and calcium transport. Kidney Int 40:1177–1189
Savage T, Clarke AL, Giles M, Tomson CR, Raine AE (1998) Calcified plaque is common in the carotid and femoral arteries of dialysis patients without clinical vascular disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:2004–2012
Jono S, McKee MD, Murry CE, Shioi A, Nishizawa Y, Mori K, Morii H, Giachelli CM (2000) Phosphate regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. Circ Res 87:e10–e17
Ketteler M, Schlieper G, Floege J (2006) Calcification and cardiovascular health: new insights into an old phenomenon. Hypertension 47:1027–1034
Moe SM, Reslerova M, Ketteler M, O'Neill K, Duan D, Koczman J, Westenfeld R, Jahnen-Dechent W, Chen NX (2005) Role of calcification inhibitors in the pathogenesis of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Kidney Int 67:2295–2304
Linhartova K, Filipovsky J, Cerbak R, Sterbakova G, Hanisová I, Beranek V (2007) Severe aortic stenosis and its association with hypertension: analysis of clinical and echocardiographic parameters. Blood Pressure 16(2):122–128
Demer LL, Tintut Y (2008) Vascular calcification: pathobiology of a multifaceted disease. Circulation 117:2938–2948
Zipes DP, Libby P, Bonow RO, Braunwald E (2005) Braunwald's heart disease, 7th edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia
Bostrom K, Watson KE, Stanford WP, Demer LL (1995) Atherosclerotic calcification: relation to developmental osteogenesis. Am J Cardiol 75:88B–91B
Mohler ER III, Gannon F, Reynolds C, Zimmerman R, Keane MG, Kaplan FS (2001) Bone formation and inflammation in cardiac valves. Circulation 103:1522–1528
Rabkin E, Aikawa M, Stone JR, Fukumoto Y, Libby P, Schoen FJ (2001) Activated interstitial myofibroblasts express catabolic enzymes and mediate matrix remodeling in myxomatous heart valves. Circulation 104:2525–2532
Rajamnnan NM, Subramaniam M, Rickard D, Stock RS, Donovan J, Springett M, Orszulak T, Fullerton DA, Tajik AJ, Bonow RO, Spelsberg T (2003) Human aortic valve calcification is associated with an osteoblast phenotype. Circulation 107:2181–2184
Lehmann S, Walther T, Kempfert J, Rastan JA, Garbage Dhein S, Mohr FW (2009) Mechanical strain and the aortic valve: influence on fibroblasts, extracellular matrix, and potential stenosis. Ann Thorac Surg 88:1476–1483
Kadena J, Dempflea CE, Grobholza R, Fischera CS, Vockea DC, Kılıça R, Sarıkoça A, Piñola R, Hagla S, Langa S, Brueckmanna M, Borggrefea M (2005) Inflammatory regulation of extracellular matrix remodeling in calcific aortic valve stenosis. Cardiovasc Pathol 14(2):80
Cui Z, Dewey S, Gomes AV (2011) Cardioproteomics: advancing the discovery of signaling mechanisms involved in cardiovascular diseases. Am J Cardiovasc Dis 1(3):274–292
Gil-Dones F, Martin-Rojas T, Lopez-Almodovar LF, de la Cuesta F, Darde VM, Alvarez-Llamas G, Juarez-Tosina R, Barroso G, Vivanco F, Padial LR, Barderas MG (2010) Valvular aortic stenosis: a proteomic insight. Clin Med Insights Cardiol 4:1–7
Freeman RV, Otto CM (2005) Spectrum of calcific aortic valve disease: pathogenesis, disease progression and treatment strategies. Circulation 111:3316
Goldbarg SH, Elmariah S, Miller MA (2007) Insights into degenerative aortic valve disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 50:1205
O'Brien KD (2006) Pathogenesis of calcific aortic valve disease: a dinase process comes of age (and a good deal more). Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:1721
Hynek R, Kuckova S, Konik P, Prchlikova R, Kodicek M (2011) A novel approach to protein analysis in hard tissues. J Surface Anal 17(3):310–313
Hynek R, Kuckova S, Hradilova J, Kodicek M (2004) Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry as a tool for fast identification of protein binders in color layers of paintings. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18(17):1896
Kuckova S, Crhova M, Vankova L, Hnizda A, Hynek R, Kodicek M (2009) Towards proteomic analysis of milk proteins in historical building materials. Int J Mass Spectrom 284:42–46
Kuckova S, Hynek R, Kodicek M (2009) Application of peptide mass mapping on proteins in historical mortars. J Cult Heri 10(2):244
Kuckova S, Sandu ICA, Crhova M, Hynek R, Fogas I, Schafer S (2013) Protein identification and localization using mass spectrometry and staining tests in cross-sections of polychrome samples. J Cult Heri 14(1):31–37
Zeman A, Šmíd M, Havelcová M, Coufalová L, Kučková Š, Velčovská M, Hynek R (2013). The structure and material composition of ossified aortic valves identified using a set of scientific methods. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.07.001
Arnaud P, Kalabay L (2002) Alpha2-HS glycoprotein: a protein in search of a function. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 18:311–314
Grieve AG, Moss SE, Hayes MJ (2012) Annexin A2 at the interface of actin and membrane dynamics: a focus on its roles in endocytosis and cell polarization. Int J Cell Biol 2012 (852430)
Nakajima M, Kizawa H, Saitoh M, Kou I, Miyazono K, Ikegawa S (2007) Mechanisms for asporin function and regulation in articular cartilage. J Biol Chem 282:32185–32192
Lee EH, Park HJ, Jeong JH, Kim YJ, Cha DW, Kwon DK, Lee SH, Cho JY (2011) The role of asporin in mineralization of human dental pulp stem cells. J Cell Physiol 226:1676–1682
Tasheva ES, Koester A, Paulsen AQ, Garrett AS, Boyle DL, Davidson HJ, Song M, Fox N, Conrad GW (2002) Mimecan/osteoglycin-deficient mice have collagen fibril abnormalities. Mol Vis 31(8):407–415
Kampmann A, Fernández B, Deindl E, Kubin T, Pipp F, Eitenmüller I, Hoefer IE, Schaper W, Zimmermann R (2009) The proteoglycan osteoglycin/mimecan is correlated with arteriogenesis. Moll Cell Biochem 322(1–2):15–23
Atalar E, Ozturk E, Ozer N (2006) Plasma soluble osteopontin concentrations are increased in patients with rheumatic mitral stenosis and associated with the severity of mitral valve calcium. Am J Cardiol 98:817
Horiuchi K, Amizuka N, Takeshita S, Takamatsu H, Katsuura M, Ozawa H, Toyama Y, Bonewald LF, Kudo A (1999) Identification and characterization of a novel protein, periostin, with restricted expression to periosteum and periodontal ligament and increased expression by transforming growth factor β. J Bone Miner Res 14:1239–1249
Novince CM, Michalski MN, Koh AJ, Sinder BP, Entezami P, Eber MR, Pettway GJ, Rosol TJ, Wronski TJ, Kozloff KM, McCauley LK (2012) Proteoglycan 4: a dynamic regulator of skeletogenesis and parathyroid hormone skeletal anabolism. J Bone Miner Res 27:11–25
Fu H, Subramanian RR, Masters SC (2000) 14-3-3 proteins: structure, function, and regulation. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 40(1):617
Berendsena AD, Fishera LW, Kiltsa TM, Owensb RT, Robeya PG, Gutkindc JS, Younga MF (2011) Modulation of canonical Wnt signaling by the extracellular matrix component biglycan. PNAS 108(41):17022–17027
Madalina VN, Young MF, Schaefer L (2012) Biglycan: a multivalent proteoglycan providing structure and signals. J Histochem Cytochem 60:963–975
Nikitovic D, Aggelidakis J, Young MF, Iozzo RV, Karamanos NK, Tzanakakis GN (2012) The biology of small leucine-rich proteoglycans in bone pathophysiology. J Biol Chem 287:33926–33933
Unsold C, Hyytiainen M, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Keski-Oja J (2001) Latent TGF-beta binding protein LTBP-1 contains three potential extracellular matrix interacting domains. J Cell Sci 114:187–197
Gualandris A, Annes JP, Arese M, Noguera I, JurukovskiV RDB (2000) The latent transforming growth factor-β-binding protein-1 promotes in vitro differentiation of embryonic stem cells into endothelium. Mol Biol Cell 11(12):4295–4308
Tunheim Engebretsen KV, Wæhre A, Lagethon Bjørnstad J, Skrbic B, Sjaastad I, Behmen D, Marstein HS, Yndestad A, Aukrust P, Christensen G, Tønnessen T (2012) Decorin, lumican and their GAG-chain synthesizing enzymes are regulated in myocardial remodeling and reverse remodeling in the mouse. J Appl Physiol 114(8):988–997
Matheson S, Larjava H, Häkkinen L (2005) Distinctive localization and function for lumican, fibromodulin and decorin to regulate collagen fibril organization in periodontal tissues. Journal of Periodontal Research 40:312–324
Luo G, Ducy P, McKee MD, Pinero GJ, Loyer E, Behringer RR, Karsenty G (1997) Spontaneous calcification of arteries and cartilage in mice lacking matrix GLA protein. Nature 386(6620):78–81
Doherty TM, Fitzpatrick LA, Inoue D, Qiao JH, Fishbein MC, Detrano RC, Shah PK, Rajavashisth TB (2004) Molecular, endocrine, and genetic mechanisms of arterial calcification. Endocr Rev 25:629–672
Zebboudj AF, Imura M, Boström K (2002) Matrix GLA protein, a regulatory protein for bone morphogenetic protein-2. J Biol Chem 277:4388–4394
Muszbek L, Bereczky Z, Bagoly Z, Komáromi I, Katona E (2011) Factor XIII: a coagulation factor with multiple plasmatic and cellular functions. Physiol Rev 91(3):931–972
George M, Ying G, Rainey MA, Solomon A, Parikh PT, Gao Q, Band V, Band H (2007) Shared as well as distinct roles of EHD proteins revealed by biochemical and functional comparisons in mammalian cells and C. elegans. BMC Cell Biol 8:3–3
Khan SR (2013) Reactive oxygen species as the molecular modulators of calcium oxalate kidney stone formation: evidence from clinical and experimental investigations. J Urol 189(3):803–811
Nishi N, Abe A, Iwaki J, Yoshida H, Itoh A, Shoji H, Kamitori S, Hirabayashi J, Nakamura T (2008) Functional and structural bases of a cysteine-less mutant as a long-lasting substitute for galectin-1. Glycobiology 18:1065–1073
Wight TN (2002) Versican: a versatile extracellular matrix proteoglycan in cell biology. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 14(5):617–6231
Zhang Y, Cao L, Kiani C, Yang BL, Hu W, Yang BB (1999) Promotion of chondrocyte proliferation by versican mediated by G1 domain and EGF-like motifs. J Cell Biochem 73:445–457
Chan KL (2003) Is aortic stenosis a preventable disease? J Am Coll Cardiol 42:593–599
Natarajan P, Kausik KR, Christopher P (2010) Cannon high-density lipoprotein and coronary heart disease: current and future therapies. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:1283–1299
Kannel WB, Castelli WP, Gordon T, Mcnamara PM (1971) Serum cholesterol, lipoproteins, and the risk of coronary heart disease: the Framingham Study. Ann Intern Med 74(1):1–12
Sharrett AR, Ballantyne CM, Coady SA, Heiss G, Sorlie PD, Catellier D, Patsch W (2001) Coronary heart disease prediction from lipoprotein cholesterol levels, triglycerides, lipoprotein(a), apolipoproteins A-I and B, and HDL density subfractions: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Circulation 104:1108–1113
Pullinger CR, Hennessy LK, Chatterton JE, Liu W, Love JA, Mendel CM, Frost PH, Malloy MJ, Schumaker VN, Kane JP (1995) Familial ligand-defective apolipoprotein B. Identification of a new mutation that decreases LDL receptor binding affinity. J Clin Invest 95:1225–1234
Rader DJ, Alexander ET, Weibel GL, Billheimer J, Rothblat H (2009) The role of reverse cholesterol transport in animals and humans and relationship to atherosclerosis. J Lipid Res 50(Supplement):S189–S194
Cuchel M, Rader DJ (2006) Macrophage reverse cholesterol transport: key to the regression of atherosclerosis? Circulation 113:2548–2555
Segrest JP, Jones MK, De Loof H, Dashti N (2001) Structure of apolipoprotein B-100 in low density lipoproteins. J Lipid Res 42(9):1346–1367
von Eckardstein A, Holz H, Sandkamp M, Weng W, Funke H, Assmann G (1991) Apolipoprotein C-III(Lys-58–>Glu). Identification of an apolipoprotein C-III variant in a family with hyperalphalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest 87:1724–1731
Strickland DK, Kounnas MZ, Argraves WS (1995) LDL receptor-related protein: a multiligand receptor for lipoprotein and proteinase catabolism. FASEB J 9:890–898
Zhaorigetu S, Yang Z, Toma I, McCaffrey TA, Hu Chien-An A (2011) Apolipoprotein L6, induced in atherosclerotic lesions, promotes apoptosis and blocks beclin 1-dependent autophagy in atherosclerotic cells. J Biol Chem 286:27389–27398
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by Specific University Research (MSMT no. 20/2013) and Project Operational Programme Prague Competitiveness (OPPC) CZ.2.16/3.100/22197.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coufalova, L., Kuckova, S., Velcovska, M. et al. Innovative technique for the direct determination of proteins in calcified aortic valves. Anal Bioanal Chem 405, 8781–8787 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7306-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7306-2