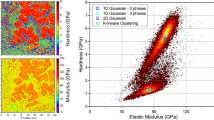
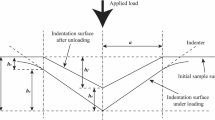
Abstract
Statistical distribution of grid indentation data measured in multiphase materials can be significantly affected by the presence of an interface between adjacent materials. The influence of an interface on the distribution of measured indentation moduli was therefore characterized in model metal–metal, ceramic–ceramic, and metal-ceramic composites. The change of properties near the interface was simulated by finite element method and experimentally verified by indentation in proximity of the boundary between two phases with distinctly different mechanical properties varying the depth of penetration and the distance from the interface. Subsequently, the conditional probability of measuring near the interface was quantified by beta distribution function with parameters dependent on the size of the volume/area affected by the presence of the interface. Using this approach, the intrinsic properties of the individual materials were successfully extracted from the experimental grid indentation data.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.F. Doerner and W.D. Nix: A method for interpreting the data from depth-sensing indentation instruments. J. Mater. Res. 1, 601 (1986).
J. Menčík, D. Munz, E. Quandt, E.R. Weppelmann, and M.V. Swain: Determination of elastic-modulus of thin-layers using nanoindentation. J. Mater. Res. 12, 2475 (1997).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: Improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 19, 3 (2004).
ISO 14577-1: Metallic materials - Instrumented indentation test for hardness and materials parameters - Part 1: Test method (ISO 14577-1:2015).
I.N. Sneddon: The relation between load and penetration in the axisymmetric Boussinesq problem for a punch of arbitrary profile. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 3, 47 (1965).
G. Constantinides, K.S. Ravi Chandran, F-J. Ulm, and K.J. Van Vliet: Grid indentation analysis of composite microstructure and mechanics: Principles and validation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 430, 189 (2006).
N.X. Randall, M. Vandamme, and F-J. Ulm: Nanoindentation analysis as a two-dimensional tool for mapping the mechanical properties of complex surfaces. J. Mater. Res. 24, 679 (2009).
K. Durst, M. Göken, and H. Vehoff: Finite element study for nanoindentation measurements on two-phase materials. J. Mater. Res. 19, 85–94 (2004).
P. Haušild, J. Nohava, and P. Pilvin: Characterisation of strain-induced martensite in a metastable austenitic stainless steel by nanoindentation. Strain 47, 129 (2011).
J. Nohava, P. Haušild, Š. Houdková, and R. Enžl: Comparison of isolated indentation and grid indentation methods for HVOF sprayed cermets. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 21, 651 (2012).
J.J. Vlassak and W.D. Nix: Indentation modulus of elastically anisotropic half spaces. Philos. Mag. A 67, 1045 (1993).
J.J. Vlassak and W.D. Nix: Measuring the elastic properties of anisotropic materials by means of indentation experiments. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 42, 1223 (1994).
P. Haušild, A. Materna, and J. Nohava: Characterization of anisotropy in hardness and indentation modulus by nanoindentation. Metallogr., Microstruct., Anal. 3, 5 (2014).
A. Materna, P. Haušild, and J. Nohava: A numerical investigation of the effect of cubic crystals orientation on the indentation modulus. Acta Physica Polonica, A 128, 693 (2015).
J. Menčík and M.V. Swain: Characterisation of materials using micro-indentation tests with pointed indenters. Mater. Forum 18, 277 (1994).
J. Menčík and M.V. Swain: Errors associated with depth-sensing microindentation tests. J. Mater. Res. 10, 1491 (1995).
A.C. Fischer-Cripps: Nanoindentation, 3rd ed. (Springer, New York, 2011).
J.C. Hay, A. Bolshakov, and G.M. Pharr: A critical examination of the fundamental relations used in the analysis of nanoindentation data. J. Mater. Res. 14, 2296 (1999).
Marc 2015: Volume A, Theory and User Information (MSC.Software Corporation, Newport Beach, 2015).
J. Matějíček, B. Nevrlá, J. Čech, M. Vilémová, V. Klevarová, and P. Haušild: Mechanical and thermal properties of individual phases formed in sintered tungsten-steel composites. Acta Physica Polonica, A 128, 718 (2015).
R.M. Christensen: Mechanics of Composite Materials (Wiley, New York, 1979).
E. Lassner and W-D. Schubert: Tungsten: Properties, Chemistry, Technology of the Element, Alloys, and Chemical Compounds (Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, 1999).
V. Brožek, P. Ctibor, J. Matějíček, R. Mušálek, and Z. Weiss: Tungsten coatings and free standing parts. In Proc.: Metal 2013, Tanger: Brno, Czech Republic, 2013; p. 6.
J.F. Shackelford, and W. Alexander: CRC Materials Science and Engineering Handbook, 3rd ed. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2001).
D. Leisen, I. Kerkamm, E. Bohn, and M. Kamlah: A novel and simple approach for characterizing the Young’s modulus of single particles in a soft matrix by nanoindentation. J. Mater. Res. 27, 3073 (2012).
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was carried out in the frame of the research project 14-36566 G (Czech Science Foundation).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haušild, P., Materna, A., Kocmanová, L. et al. Determination of the individual phase properties from the measured grid indentation data. Journal of Materials Research 31, 3538–3548 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.375
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.375